本文首先,进行了离群值检查,并从外国直接投资和交通基础设施中排除了105项观察。这导致这两个变量的描述性统计以及所有变量之间的相关性发生变化。Jarque-Bera检验表明变量不是正态分布的。然而,对于经济面板数据来说,这是一种普遍现象,大多数估计方法都能解决这一问题。然后,对记录的变量进行了面板Granger因果关系检验,在14种关系中,6种关系没有Granger因果关系。我们还发现,市场规模与FDI、资源与FDI之间存在格兰杰因果关系。除开放性外,其他自变量均由Granger引起。
CHAPTER ONE. Introduction
1.1) Original points of thesis
While there are many works regarding the relationship between infrastructure and FDI,the following gaps were found: the previous studies analyzed either a particular countryor some specific groups of countries (e.g. Sub-Saharan (SSA) countries). For our ac-knowledgment, the latest study that analyzed the relationship between infrastructure andforeign direct investment for the whole world was conducted more than a decade ago byGoodspeed, Martinez-Vazquez, and Zhang (2006). Yet, they used data only for eightyears and included only one country from Africa in a sample.
This study represents the whole world analysis using countries from different re-gions and with different levels of economic development. While many panel analysesneglect newly industrialized countries (NIC), which play a significant role in the modernworld, we have included them in the sample to achieve a complete picture on the de-pendence of FDI on infrastructure in the world.
Another interesting gap is that only a few scholars have used electricity infra-structure as a determinant of FDI (Ayanwale, 2007; Bellak, Leibrecht and Damijian,2009). While Ayanwale (2007) showed the importance of electricity for Nigerian case,Bellak, Leibrecht and Damijian (2009) concluded that it is less important than telecom-munication and transport infrastructure. The inclusion of this variable to this studyhelped us to put forward a new opinion on the significance of this variable in the world.
The work used the newest available (throughout the period from 1996 to 2017)data and more advanced empirical technologies. While scholars used just the ordinaryleast squares (OLS) and Fixed or Random Effect models to address the question, we alsoapplied robust methods like general method of moments (GMM) and robust least squares.
..........................
1.2) Limitations
Like any work, the study faced some limitations. First of all, data was not available formany countries, which resulted in unbalanced data and reduced the number of observa-tions. However, this problem is quite common for economic researches.
Second limitation was that only four control variables were included in the re-gression. The reason for that was to understand the significance of infrastructure, com-pared to openness and resources. However, there are more possible variables that canhelp capture the relationship between infrastructure and foreign direct investment.
The last but not the least limitation was that the sample was not split into threecategories depending on the different levels of economic development. One of the rea-sons is that the study was concentrated on the relationship between infrastructure and FDI in the whole world. Another reason was that the number of countries in each sub-sample and the number of observations was not enough to conduct an unbiased analysis.
...........................
CHAPTER TWO. Literature review
2.1) Theoretical aspects of FDI
As was said before, there are two classical types of foreign direct investment, horizontaland vertical. Yet, some scholars identify two more types, conglomerate and platform FDI.Conglomerate FDI is an investment to a foreign company, which business is unrelated tothe business of the investor company. Platform FDI also called export-platform FDI,means that all the output produced in the host country will be exported to a third country.
The classification outlined above is not the only one. There are other classifica-tions, which are discussed below. Considering the motives for investment, FDI can bedivided into three categories: market-seeking, resource-seeking, and efficiency-seeking.
Resource-seeking means investing in countries that have more affordable re-sources. By resources, we do not just consider natural resources, e.g. minerals, but alsolabor resources, often unskilled and low-cost. Market-seeking is the type of investmentthat considers the market size, income per capita as essential determinants of FDI. Effi-ciency-seeking is an attempt to use the advantages of a country’s political system, regula-tions, and traditions to rationalize a firm’s production.
Regarding the methods of foreign direct investment, scholars usually distinguishthe following four types: mergers and acquisition; joint ventures; shares acquisition; asubsidiary.
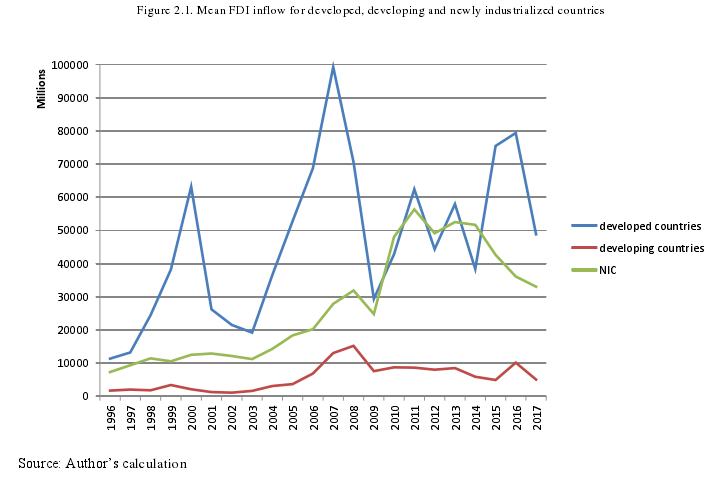
Figure 2.1. Mean FDI inflow for developed, developing and newly industrialized countries
CHAPTER ONE. Introduction
1.1) Original points of thesis
While there are many works regarding the relationship between infrastructure and FDI,the following gaps were found: the previous studies analyzed either a particular countryor some specific groups of countries (e.g. Sub-Saharan (SSA) countries). For our ac-knowledgment, the latest study that analyzed the relationship between infrastructure andforeign direct investment for the whole world was conducted more than a decade ago byGoodspeed, Martinez-Vazquez, and Zhang (2006). Yet, they used data only for eightyears and included only one country from Africa in a sample.
This study represents the whole world analysis using countries from different re-gions and with different levels of economic development. While many panel analysesneglect newly industrialized countries (NIC), which play a significant role in the modernworld, we have included them in the sample to achieve a complete picture on the de-pendence of FDI on infrastructure in the world.
Another interesting gap is that only a few scholars have used electricity infra-structure as a determinant of FDI (Ayanwale, 2007; Bellak, Leibrecht and Damijian,2009). While Ayanwale (2007) showed the importance of electricity for Nigerian case,Bellak, Leibrecht and Damijian (2009) concluded that it is less important than telecom-munication and transport infrastructure. The inclusion of this variable to this studyhelped us to put forward a new opinion on the significance of this variable in the world.
The work used the newest available (throughout the period from 1996 to 2017)data and more advanced empirical technologies. While scholars used just the ordinaryleast squares (OLS) and Fixed or Random Effect models to address the question, we alsoapplied robust methods like general method of moments (GMM) and robust least squares.
..........................
1.2) Limitations
Like any work, the study faced some limitations. First of all, data was not available formany countries, which resulted in unbalanced data and reduced the number of observa-tions. However, this problem is quite common for economic researches.
Second limitation was that only four control variables were included in the re-gression. The reason for that was to understand the significance of infrastructure, com-pared to openness and resources. However, there are more possible variables that canhelp capture the relationship between infrastructure and foreign direct investment.
The last but not the least limitation was that the sample was not split into threecategories depending on the different levels of economic development. One of the rea-sons is that the study was concentrated on the relationship between infrastructure and FDI in the whole world. Another reason was that the number of countries in each sub-sample and the number of observations was not enough to conduct an unbiased analysis.
...........................
CHAPTER TWO. Literature review
2.1) Theoretical aspects of FDI
As was said before, there are two classical types of foreign direct investment, horizontaland vertical. Yet, some scholars identify two more types, conglomerate and platform FDI.Conglomerate FDI is an investment to a foreign company, which business is unrelated tothe business of the investor company. Platform FDI also called export-platform FDI,means that all the output produced in the host country will be exported to a third country.
The classification outlined above is not the only one. There are other classifica-tions, which are discussed below. Considering the motives for investment, FDI can bedivided into three categories: market-seeking, resource-seeking, and efficiency-seeking.
Resource-seeking means investing in countries that have more affordable re-sources. By resources, we do not just consider natural resources, e.g. minerals, but alsolabor resources, often unskilled and low-cost. Market-seeking is the type of investmentthat considers the market size, income per capita as essential determinants of FDI. Effi-ciency-seeking is an attempt to use the advantages of a country’s political system, regula-tions, and traditions to rationalize a firm’s production.
Regarding the methods of foreign direct investment, scholars usually distinguishthe following four types: mergers and acquisition; joint ventures; shares acquisition; asubsidiary.

Figure 2.1. Mean FDI inflow for developed, developing and newly industrialized countries
.......................
2.2) Infrastructure and FDI: theoretical aspects
Giving all theoretical information regarding foreign direct investment we can concludethat investors tend to search for the markets where they can maximize benefits or de-crease the production cost. They can achieve these goals if infrastructure is developed.
FDI tends to occur in countries with a more developed level of physical infra-structure, like bridges, roads, and so on. Of course, many countries with poor infrastruc-ture can be unattractive for other reasons, but if everything is equal, the country withmore developed infrastructure will receive more investment, domestic and foreign.
Von Thunen’s model shows that an improvement in transportation infrastructureresults in the declining transportation cost of agricultural production. Edwards (2011)reckoned that a potential firm could not innovate when the area did not have well-developed infrastructure. He believed that if a government wanted to attract new firms,new infrastructure should be constructed.
It is also a well-known fact that public infrastructure indirectly reduces the pro-duction cost of a firm. As infrastructure becomes more reliable and secure, foreign com-panies can facilitate access to the production inputs and better serve the market.
Moreover, governments cannot develop just one type of infrastructure. While, forexample, telecommunication infrastructure is required for sustainable growth, it cannotsubstitute transportation infrastructure.
From a brief review, it is evident that infrastructure is important in attracting FDI.The research work was aimed to investigate, on a macroeconomic level, whether or not,there are real effects of physical infrastructure on foreign direct investment.
........................
2.2) Infrastructure and FDI: theoretical aspects
Giving all theoretical information regarding foreign direct investment we can concludethat investors tend to search for the markets where they can maximize benefits or de-crease the production cost. They can achieve these goals if infrastructure is developed.
FDI tends to occur in countries with a more developed level of physical infra-structure, like bridges, roads, and so on. Of course, many countries with poor infrastruc-ture can be unattractive for other reasons, but if everything is equal, the country withmore developed infrastructure will receive more investment, domestic and foreign.
Von Thunen’s model shows that an improvement in transportation infrastructureresults in the declining transportation cost of agricultural production. Edwards (2011)reckoned that a potential firm could not innovate when the area did not have well-developed infrastructure. He believed that if a government wanted to attract new firms,new infrastructure should be constructed.
It is also a well-known fact that public infrastructure indirectly reduces the pro-duction cost of a firm. As infrastructure becomes more reliable and secure, foreign com-panies can facilitate access to the production inputs and better serve the market.
Moreover, governments cannot develop just one type of infrastructure. While, forexample, telecommunication infrastructure is required for sustainable growth, it cannotsubstitute transportation infrastructure.
From a brief review, it is evident that infrastructure is important in attracting FDI.The research work was aimed to investigate, on a macroeconomic level, whether or not,there are real effects of physical infrastructure on foreign direct investment.
........................
CHAPTER THREE: METHODOLOGY……………………15
3.1) Variables and Data…………………………16
3.1.1) Infrastructure………………...…16
3.1.2) Foreign Direct Investment………………………….20
CHAPTER FOUR: EMPIRICAL RESULTS…………………….25
4.1) Outliers check……………………….25
4.2) Descriptive statistics………………………28
CHAPTER FIVE: FORECASTING…………………47
CHAPTER FIVE. Forecasting
Since the three models, the fixed-effect model, robust least squares and GMM, wereestimated to analyze the relationship between infrastructure and FDI, it was essentialto understand how these models fit the data.
R2is considered to evaluate how the independent variables predict the de-pendent one. However, R2becomes an unimportant statistic in the case of GMM. An-other problem is that R2suffers a spatial autocorrelation problem, so we might bevery cautious in interpreting the results using R2.
Another possible solution to this is the residual graph. Residual is the verticaldistance between the actual and fitted data points. The residuals can be positive andnegative. If the fitted data passes the actual, then the residual is zero. There are twotypes of residual representation, a table, and a graph. While the numerical method isalso useful, the graphical method visualizes the relationship between the data andmodel, thus making the analysis easier. The residuals graphs for the three models arerepresented in the Appendix. As can be seen from the graph, RobustLS predicts FDIvery poorly. Thus it is not appropriate for our data set.
If we compare the fixed-effect model and GMM, we can find that GMM re-siduals are more distributed around 0. However, GMM residuals have more outliers,especially for the Italian case.
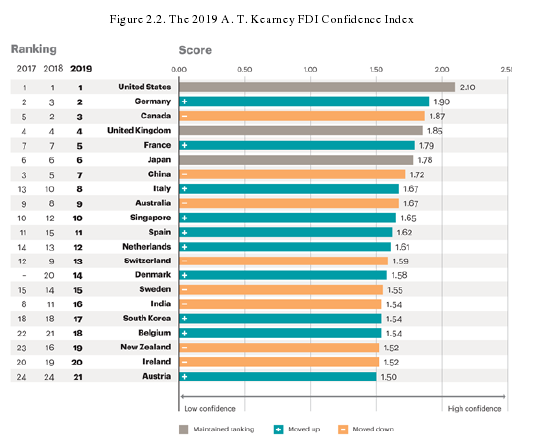
Figure 2.2. The 2019 A. T. Kearney FDI Confidence Index
CHAPTER SIX. Conclusions
The thesis aimed to analyze the relationship between FDI and three types of infra-structure, transportation, telecommunication, and electricity in the world. To achieve this, the econometric model was estimated with the addition of four variables, marketsize, openness, the skill level of labor, and abundance of resources. The proxies forthe variables were chosen in accordance with the existing literature.
First, the outliers check was done, and 105 observations were excluded fromFDI and transportation infrastructure. This resulted in the change in the descriptivestatistics for these two variables and the correlation between the all variables.
Jarque-Bera test showed that variables are not normally distributed. However,it is common for economic panel data and most estimation methods can deal with thisproblem.
Then, the panel Granger Causality test was conducted for logged variables.Among the 14 relationships, it was found no Granger causality for the six relation-ships. We also found that the market size and FDI, resources and FDI Granger causedeach other. All other independent variables, except for openness, Granger caused thedependent variables.
The next step was to test the stationarity of the variables via the Unit RootTest. It was found that all the variables, logged and not logged, are stationary at thefirst difference. As for the stationarity at level, we couldn’t reject the null hypothesisof the presence of individual unit root for the market size. Regarding transportation,the skill level of labor and openness, the rejection of the null hypothesis depends onthe test we used. We also rejected the null hypothesis for the logged openness.
reference(omitted)
