本研究的统计结果表明,中国政府的自由化努力与外资寿险公司较高的市场份额正相关,保险密度和劳动人口数量将是中国走向更高竞争的积极驱动力。根据这些实证结果、市场专家的发言和最新消息,可以说,外国寿险公司很有可能在未来在中国扮演更重要的角色,并像以前一样获得更高的市场份额。这将主要取决于他们的商业战略,即如何利用巨大的市场潜力,接触到中国客户,以及中国政府是否会继续朝着更加开放和自由的经济发展。
1. Chinese Insurance Industry
1.1Overview
After the Chinese economic reform gaige kaifang 改革开放 led by Deng Xiaoping in1978, opening China to the outside world, the Chinese macroeconomy has developedby a rapid growth rate.10Between 1980 and 2009, Chinas real gross domestic productgrowth annually at an average rate of 9.7 percent. This was significantly above theglobal average growth rate over the same period over these nearly three decades. Thesignificant economic growth of China considerably affected all of its industrial andtechnological sectors, consequently shaping China to be one of the most importanteconomies. This is a unique and unparalleled growth story from a developing countryto one of the largest global economies in just three decades.
In 1978 there was no insurance industry in China, besides the state self-insured.11Sincethe early 1990s, however, a policy change led to growth rates of the insurance industrythat were more than twice as high as the growth rate of China’s gross domestic product.This was one of the results of the overall increasing Chinese economy in the lastdecades. But even with these strong growth rates and a global market share of 12% forlife- and 11% for property insurances in 201812,the industry’s current developmentandmarket penetration is still significantly low compared to international standards andother developed countries. This illustrates that there still exists a substantial additionalgrowth and improvement potential for the future, especially when considering thecurrent stage of the Chinese economy and the latest policies of the Chinese governmentto open the financial system further, thereby improving foreign capital investments intoChina and its insurance industries. As mentioned before just in 2018, the governmentremoved the foreign ownership limits for companies related to the banking and insurance industry which will make it possible for foreign insurers to take higher equitystakes in companies and receive more substantial participation rates when it comes tonot only (i) investment decisions, but also (ii) government decisions.13A potentialoutcome of this could be more intense competition, thereby improving the overallquality and pricing of insurance products and services which should in turn presumablylead to a higher penetrated and developed insurance market and further growingChinese insurance industry, especially considering how vital insurance products andservices are for certain parts of the economy as it lowers the monetary impact ofadversary tail events (large insurance events such as natural disasters, data breaches,key person failure to name a few).
...........................
1.2 Historical Development
As highlighted before, the People’s Republic of China had basically no insuranceindustry in the past.14After the foundation of the PRC in 1949, the governmentestablished the People’s Insurance Company of China (PICC), a state-owned insurerthat replaced all other insurance companies subsequently and led to a monopolyposition in 1956. Before 1949, the Chinese insurance market was controlled by foreigncompanies operating in Shanghai. 43 of all 58 insurers were privately owned. Themonopoly position of the PICC, as well as the government’s policy impairs thedevelopment of the Chinese insurance industry for the following two decades until1978. During that time the business scope was limited to international cargo andaviation insurance products and services. As a part of the economic reforms and“opening doors” policies, the insurance industry was reformed.15The PICC wasreestablished, market incentives and risk management started to be recognized asimportant factors and the company became more open for other kinds of insurance products and services, thereby increasing its product portfolio and insurance coverage.Through the following decade, the PICC was very profitable and grew by a substantialrate.
The monopoly position ended in the late 1980s, when other insurance companies suchas the Xinjiang Agriculture Insurance Company (1987), Ping An Insurance Company(1988) and the China Pacific Insurance Company (1991) were founded. The firstforeign insurance companies entered the market in the early 1990s under strictregulations, which depended, among others, on certain conditions imposed by the stateincluding that the majority stake of the insurance companies would need to be kept byeither the Chinese government or Chinese corporations. The first company was theAmerican International Group (AIG), at this time the largest insurer in the world.
..........................
2 Research Design
2.1Statistical Model and Variables
The results of existing research illustrate the large potential of the Chinese insurancemarket, the factors for demand and the advantages and disadvantages of foreigncompanies. It is already proven that foreign companies working more efficiently, butcurrently they are not able to get a higher profit efficiency and more market share inChina.
The aim of the statistical analysis is to see which variables affecting the market shareof foreign companies in domestic markets in general. This should clarify the possiblereasons for the current situation in China and allow a forecast for the future. Thestatistically significant factors, influencing the foreign market share positively ornegatively, can be analysed for the Chinese market to see how the prospectivedevelopment could be. To ensure that the results will be valid the sample size shouldbe large enough and cover a longer time period for the respective markets.
The basic idea of the model is influenced by the research from Yu-Luen Ma and NatPope (2008). Their research paper analysed the market characteristics that attractinternational life insurer’s participation. To make this model suitable for this specificresearch question it was necessary to make some adjustments. The dependent variableis FOREIGNSHARE describing the market share of foreign life insurance companiesin the respective countries. The regression analysis will test which other variables are correlating with the foreign market share and the empirical equation can be written asfollows:
FOREIGNSHAREi,t= f(MARKETSIZEi,t, LIBERALi,t, GDPi,t, DENSITYi,t,EMPLOYEESi,t, SURVIVORi,t, RETIREMENTi,t, WORKINGi,t, EQUITYRESi,t,SCREENANDAPPRi,t, KEYFORPERSi,t, OTHERRESi,t),
...........................
2.2 Sample Size and Data Collection
Sample SizeThe sample size includes the data of 49 OECD and non-OECD countries for the timeperiod from 2007 to 2017. So the research covers countries from a diverse backgroundin terms of economic development, population and geographical region. This largesample size should ensure that the results are valid and the statistically significantvariables will have an impact of the market share of foreign life insurance companies,regardless in which specific country they plan to expand. The included countries arelisted down below:
Asia-Pacific: Australia, Japan, South-Korea, Malaysia, India, Singapore.
Europe: Austria, Czech-Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Greece,Hungary, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Norway,Poland, Portugal, Slovak-Republic, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, United-Kingdom, Russia.
America: Canada, Mexico, United-States, Puerto-Rico, Chile, Argentina, Bolivia,Brazil, Columbia, Paraguay, Peru, Uruguay, Costa Rica, El-Salvador, Nicaragua.
Middle East: Israel.
Western Asia: Turkey.
Africa: South Africa.
Most of the countries are located in Europe, America and the most important Countriesin Asia-Pacific (excluded China). The sample is ranging from highly developed butalready saturated insurance industries like the United-States, Japan and Germany touprising markets with strong growth rates, like the Latin American countries and India.Furthermore, these countries are very different in terms of the Government restrictionslimiting foreign companies to enter the market. The results will show if these measuresaffect the foreign share significantly or if some other factors are important as well.
Dependent Variable = Foreignshare
............................
3. Literature Review ...........................13
4. Research Design ...............................15
4.1 Statistical Model and Variables ...................15
4.2 Sample Size and Data Collection ...............................21
5. Results ............................22
5.1 Statistical Results in Numbers ...............................22
5.2 Interpretation of the Results for the Chinese Insurance Market ........................25
5. Results
5.1 Statistical Results in Numbers
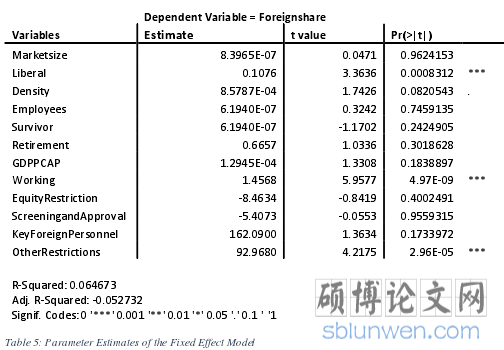
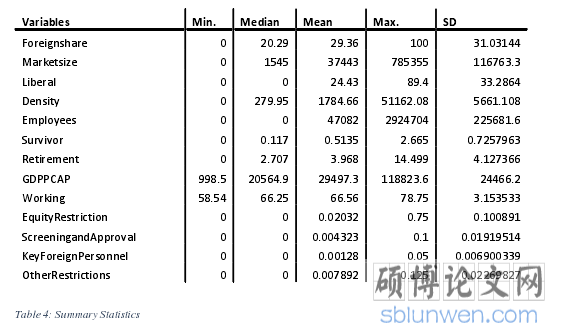
The empirical results, showing the mean, median, max, min, standard deviation as wellas the parameter estimates, are presented in the following tables and it can be seen thatsome of the variables are statistically significant and influencing the market share offoreign life insurance companies in domestic markets around the world.
取消中国保险业的外资所有权限制:新比赛开始了吗?
6. Conclusion
According to all statistical indicators, the leading experts of the industry and the latestpolicies, there is no doubt that the Chinese insurance industry is currently the mostpromising in the world. No other market has a comparable situation which such a highmarket potential. So every large international insurance company like Allianz, AXA,or Generali, just to name a few, will have to become successful in China to keep theirpositions as leading insurers globally. The strong development of the two largestChinese players PingAn Insurance and China Life Insurance is an example of theimportance of the Chinese market. Both companies are mainly focussing their businessactivities just in China and became the largest (PingAn Insurance) and 5thlargest(China Life Insurance) insurance companies in the world, while firms like Allianz areworking in more than 70 countries around the world38and became smaller than theChinese market leaders.
Foreign companies are aware of this situation and will increase their business activitiesin China and according to the latest policies of the CBIRC, China wants them to playa more important role. The French insurer Axa has already bought the 50% of theChinese joint venture Axa Tianping and Allianz got the approval to open up a wholly-owned holding company based in Shanghai.39Also Generali (Italy) and Prudential (UK)are planning to use the new policy to increase their stakes in their local joint ventures.And probably many more will follow.
reference(omitted)
