笔者认为贸易开放和投资对南掸邦的经济增长有积极影响。通货膨胀与经济增长呈负相关关系,这与托宾(1965)的理论相矛盾,但支持斯托克曼(1981)的通货膨胀与经济增长观。瓦格纳’政府支出和政府支出的平方分别呈现正的和负的变化,证实了s定律。
Chapter One Introduction
1.1 Background and Significance
1.1.1 Background
The financial system in Africa is not robust and might not stand the test of time. Anunsound financial system usually results in financial crisis, which inherently has negativeconsequences for growth. An example can be made of the financial crisis which happenedin the USA which did not only affect the economic growth of USA but had a negativespill over effect in some Asian and European economies. As posited by Sundararajan,Balino, Bali o, and Bali o (1991), views crisis in the financial sector as a state whereby anumber of financial institutions have huge debt which they are unable to payback as itoutweighs the market value of their assets, the fall down of some financial institutions andgovernment involvement to intercede in the such events. There is high level of exchangerate problems and interest rates which discourages investment decisions. In such events,non-performance of loans are always on the rise as the economic conditions becomeunfavourable, thus create problems for the financial sector.
Cheang (2004) stressed that, the existence of financial stability in an economy is thefirst priority investors, specifically foreign investors look at before they enter thedomestic market of a country to establish business. When foreign businesses areestablished, there is usually enough inflow of foreign capital which can lead to moreeconomic activities and increase demand in labour. To establish a strong financial system,countries in Africa have undergone several finance reforms with the aim of strengtheningthe finance system in the past and in the present times. Believed to be a significant portionof macroeconomic policy, the finance sector reforms are supposed to augment importanteconomic merits, specifically by means of a more potent and efficient saving mobilizationinternally and an enhanced way of earmarking funds Khan, Qayyum, Sheikh, andSiddique (2005). Although, critical efforts have been made by African countries, theseefforts have been inadequate as the financial system is still weak which is evidenced inmany of the countries in Africa continent.
........................
1.2 Organization of the Study
The study is in six chapters. This first chapter discusses the background of the study,statement of the problem, objectives, research questions, justification of the study,significance of the study and scope and limitations. The second chapter will deal with thereview of relevant literature: both theoretical and empirical. The third chapter will dealwith the financial sector and economic growth in Sub-Saharan Africa. Chapter fourdiscusses the research methodology. Chapter five will deal with the estimation anddiscussion of results of the study and the last chapter (chapter six) is dedicated tosumming up and concluding the results of the study and recommendations for policyimplementation.
........................
Chapter Two Literature Review
2.1 Theoretical Literature
Diverse opinions are held by economists concerning the role of the financial system inpromoting economic growth. Hicks (1969) observed that, the development of the financesector played an important industrialization role in England. Studies on the relationshipbetween financial development and economic growth can be traced to Schumpeter (1911)who performed a critical research on the principal role of financial services in innovationand development. The role played by financial institutions are highly important as thereimprove the growth and development of the economy through recognising and makingmoney available for productive investments. Ahmed (2006) the financial sector plays acritical role in channelling funds from savers to investors. Thus the sector plays animportant role in wealth accumulation, trade and capital formation.
There are four views regarding financial development and economic growth. The firstview known as the supply-leading hypothesis, suggest that, financial development causeseconomic growth. Thus, the development of the financial sector will play a significantrole in the growth of an economy Schumpeter (1911);Robert G King, Levine, andintermediation (1993); and Calderón and Liu (2003). Hence, causal effect runs fromfinancial development to economic growth and not in the opposite direction. This is as aresult of high savings rate and an increase in productive investments. The second is thedemand-leading hypothesis. This view suggest that, economic growth causes financialdevelopment. Hence, when the economy is improved, the financial sector will bedeveloped Jung and change (1986); and Ireland (1994). As a result, causality runs fromeconomic growth to financial development and not in the reverse direction.
.....................
2.2 Empirical Literature
The relationship between financial development and economic growth is acontroversial issue. The area of financial development and economic growth has attracted manyresearchers to undertake a comprehensive study on the subject matter using differenteconometric methods. The first researcher to study on the area of finance and growth wasGoldsmith (1969). Goldsmith (1969) studied if banks and stock market affect growth ofan economy. Goldsmith (1969) data was based on 35 underdeveloped and developed inthe period of 1860 to 1963. He concluded from the study that, there was a positiverelationship between financial development and economic growth.
It is a fact that the development of the finance sector is a key determinant of economicgrowth Khalifa Al‐Yousif (2002); Rahaman and Finance (2011) in accordance with thepioneering work of Schumpeter (1911) and the later supposition of ‘more finance, moregrowth’ by Levine (2003). These studies however assumed the link between thepersistence of finance-growth along time or linear relationship. Several studies have however shown that the effect of financial development on economic growth is alsoconditional on many other factors rather than by itself alone. These included thethresholds of other variables such as inflation Rousseau, Wachtel, and finance (2002),government size, trade openness and income per capita Yilmazkuday (2011), policies inthe financial sector Abiad and Mody (2005); Ang (2008),legal systems La Porta et al. (1997), government ownership of bank Andrianova,Demetriades, and Shortland (2008), culture Stulz and Williamson (2003), trade andfinancial openness Law (2009); Rajan and Zingales (2003), remittances Demirguc-Kuntet al. (2011), political institutions Girma and Shortland (2008); Huang et al. (2010); Roeand Siegel (2011), and institutional quality S. H. Law and Azman-Saini (2012); Law, et al.(2018).
.............................
Chapter Four Methodology of the Study.......................27
4.1 Conceptual Framework.................................27
4.2 Operational Model.....................27
Chapter Five Estimation and Discussion of Results.............................34
5.1 Descriptive Analysis...............................34
5.2 Estimation Results............................35
Chapter Five Estimation and Discussion of Results
5.1 Descriptive Analysis
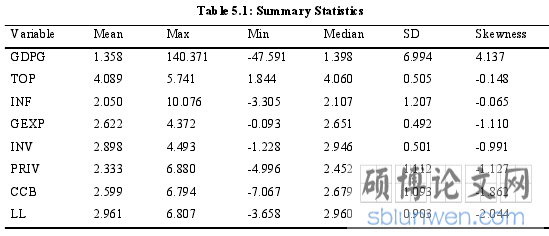
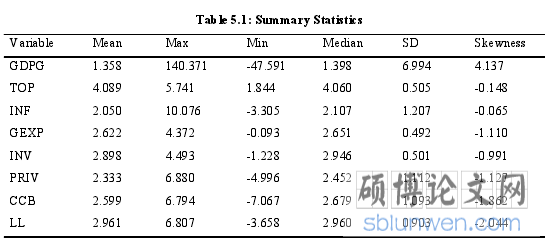
Based on the panel data from the 48 countries from Sub-Saharan Africa, the summarystatistics of the variables and the pairwise correlation between regression variables areshown in the table 5.1 and 5.2 respectively. Form table 5.1, it emerged that economicgrowth averaged 1.358 percent over the study’s time period, with a minimum ofapproximately negative 48 percent and a maximum of 140 percent. Summary statistics onmeasures of financial development and financial stability are provided. Table 5.2 revealsthat trade openness, investment and financial stability have a statistically significantpositive correlation with economic growth. As confirmed by theory, inflation has astatistically significant negative correlation with economic growth. Further governmentexpenditure and measure of financial development are also found to have a statisticallynegative correlation with economic growth.
Chapter Six Summary and Conclusions andRecommendations
6.1 Summary and Conclusion
This research sought to establish the link that exist between financial development andfinancial stability on economic growth in a sample of 48 countries of SSA over theduration of 1970–2017. Dynamic panel data techniques were applied for the study.Generalised Methods of Moments was applied to estimate the parameters of the chosenmodels.
Moreover, there exist granger causality between financial development, financialstability and economic growth which is bidirectional.
Furthermore, trade openness and investment positively affect the growth of theeconomy of SSA. Inflation showed a negative relationship on economic growth, whichcontradicts Tobin (1965) theory but supports Stockman (1981) view on inflation andeconomic growth instead. Wagner’s Law was confirmed in the study as governmentexpenditure and the square of government expenditure showed positive and negativesigns respectively.
In the future, interested researchers can include more explanatory variables regardingthe system of finance in SSA and can further extend the study to increase the sample size.This is worthwhile as financial crises experience is the past can be curbed as policy makers will be abreast with the right policies to implement and enforced to strengthen thefinancial system. Also, it can inform policy makers if S-shaped is likely to occur betweenfinancial development and economic growth in the future.
reference(omitted)
