Chapter 1 Introduction
1.1 Background
Education is usually acknowledged as an important factor of economic growth. This shows a dynamic role in human capacity building and rushes economic growth over a society's awareness, expertise and innovative power. Not only are the benefits of schooling limited to the national economy, but it also benefits individuals. Education is particularly important for the Pakistan, wherever advancement is necessary if an economy want to come out from less growth rate. Pakistan has placed great importance on elementary and just now on secondary education for several decades. But as a means of improving economic growth, they have ignored tertiary / the higher education. Pakistan?s education system has suffered the Government's ongoing and serious expenditure over the past five decades. Public education spending presently stands at 1.7 per cent of GDP, as opposed to 4 per cent of UNESCO's education spending. According to the UNDP, Pakistan is one of the world's 12 countries, investing only 2 % of GDP on education sector. Some scholars say that improving Pakistan's education could boost growth and productivity. As human capital literature rate is currently the lowest in the world. On the other side, less growth rate reduces the State's ability to provide universal education. Since Ancient Greece the interrelationships among schooling and economic development have been discussed. A different group of researchers like Adam Smith and classical economists stressed the status of investing in social capabilities. A primary effort to calculate education?s impact to economic growth was either based on the accounting method of growth or the rate of return on human resources. Though, it wasn't too late in the 20th era that this relationship was formally and scientifically analyzed by researchers. Numerous studies studied the connection among economic growth and the education, for example Psaharoupolous, 1988; De Meulmester et. al 1995; Jorgenson & Fraumeni 1998. Their initial opinion has at all times been the base of very growth of the economy. The older philosophers assumed that growth of the economy in the productive processes depended on capital increase and the labor factor. The rising productivity in these production factors was found to be a dynamic reason of economic growth. While researchers confirmed that country-wide associations exist among economic growth levels and school admission rates counting the higher education registration, a different group of scholars for example De Meulmester et al. (1995) used new innovative econometric methods, initiate that this is not a clear relation.
..........................
1.2 Problem Statement and Research Objectives
Theoretical literature predicts that employment will affect economic growth positively (Romer, 1987). Empirical research, however, shows mixed results that education impacts growth though most of the studies are agreed with this literature. The findings of whether schooling and economic growth have a causal relationship are inconclusive.
It has been noted in recent years that government is putting more emphasis on educational attainment. Government has also increased its spending on the education sector. There has been an intense increase in higher level of education enrollments since 2001. That shows that demand for education in Pakistan has been rising. The Pakistan economy, however, till now facing high poverty problem, income disparity, and poor conditions of educational institutes in the public sector, high fees paid by universities in the private sector, poor academic policies and poor implementation of those strategies. Public education spending presently stands at 1.7 per cent of GDP, as opposed to 4 per cent of UNESCO's education spending. According to the UNDP, Pakistan is one of the world's 12 countries, investing only 2% of GDP on education sector.
Pakistan's growth trend has been positive but Pakistan has not performed well enough compared with other countries like India and China. According to the IMF's international economic outlook (2014), the average annual growth rate for Pakistan between 1990 and 2011 is 2.9%, whereas comparable figures for China and India are 10.5% and 6.8% respectively. Given that here is a connection among growth of the country and the higher education as attested by theories and other previous studies, the basic aim of the research is to create the relation among Pakistan's growth of the country and education.
........................
Chapter 2 Literature Review
2.1 Education & Economic Growth
(Bashir and Amir 2019) investigate that education expenditures have significant influence on Pakistan's short-term and long-term growth of the economy, using ARDL methodology, from 1971 to 2017. Moreover, study concludes the results of error correction term that GDP per capita deviation from the equilibrium level would be rectified by about 11% each year. Based on the findings, study recommends poverty reduction and stabilization of the macroeconomics. Government intervention promoting further education spending and stimulating economic growth is of paramount importance.
Across 15,000 different universities from 78 countries, 10 percent of the region's universities were correlated with a 0.4 percent increase in that region's GDP. Additionally universities effect positively to the other neighboring counties that are close to each other .huge amount of human capital and increased invention has large-scale impact on economic growth (Valero and Reenen 2018). Study explores the influence of real GDP of Pakistan on human capital or progress from 1992 until 2014. Johansen's technique of co-integration has been used in the long run to check the influence of human capital on real GDP; study showed that the relationship between these two is positive. Education sector investment is required to improve the human capital which brings economic growth. (Kazmi, Ali and Ali 2018)
(Abugamea 2018) used the OLS calculation to analyze the effects of education in Palestine from 1990 through 2014. The study presented that secondary schooling admissions and higher education enrolments are having a decreasing and less outcome on the economic growth due to the weakness of the Palestinian economy. Improving economic growth requires quality education. Study analyzes the relationship among female high school enrollment and economic growth of Pakistan from 1975 to 2014 and Johansen Co-integration technique was applied. Study initiated that female secondary education and labor have marginal positive effects while capital increase has positive effects on economic development of Pakistan. By applying the Granger long-term causality test found between female high school enrollment and GDP while short-term unidirectional causality that runs from GDP to female high school enrollment is found (Ali, 2017).
........................
2.2 Poverty & Income Inequality
In India and China affiliation among growth of the country and education were studied by using the yearly data from the period of 1970 to 2005. The research used a dynamic ordinary least squares (DOLS) econometric techniques and also the vector errors correction model (VECM). The study results point out that China and India have a long run trend association among economic growth and education. For both countries, a one sided fundamental relationship has been noticed in the long run, in China between income and expenditure on education , while if talk about India the results showed that Granger causality is found among education spending and income (Kaur, Baharom and Habibullah, 2014).
Role of quality education is discussed in this study. Study initiated that Population with intellectual skills contributed further to economic growth then only to school achievement. A basic school education has a great influence on development of the economy, and improving the schooling structure can reduce the economic gap with industrial countries. She also suggests that addition of information technology in teaching will improve the quality of education (Kiani and Adiqa, 2013). Study examines the effects of employment, safety, and food inflation on economic growth using the 1971-1972 to 2010-2011 ARDL methodology. Study reveals the positive and negative effect respectively on food inflation and education in short- and long-term on growth of the country. Two- way causality is found between economic growth, education, and food inflation (Afzal et al, 2013).
This study considered the case of the Asian countries and modeled macroeconomic factors like human capital greatly affected the economic growth in the panel data by using the fixed and random effect model., with controlled It has been observed that by using the random effects model human capital investment has a negative influence on GDP, but no effect was found when applied fixed effects model in the study (Ullah and Rauf, 2013). The effects of higher education on economic growth of Pakistan's between 1980 and 2011 using the ARDL methodology was discussed in this study and the positive relationship found in both. Study suggests that the strengthening of the Higher Education Commission will increase economic development (Qazi et al, 2013).

...............................
Chapter 3 Education Sector in Pakistan: An Overview .................................... 23
3.1 Introduction ............................ 23
3.2 Regional Education Assessment.................. 23
Chapter 4 Data Sources and Methodology ...................................... 29
4.1 Data Sources ................................... 29
4.2 Methodology ............................. 29
Chapter 5 Results and Interpretation .................................... 31
5.1 Unit Root Test .......................................... 31
5.2 Test of Co-Integration ............................. 32
Chapter 5 Results and Interpretation
5.1 Unit Root Test
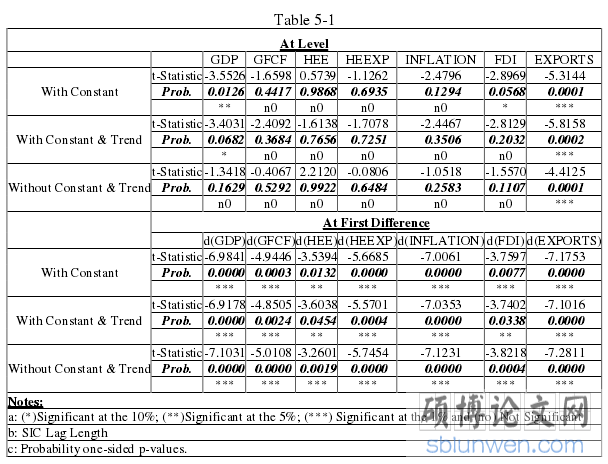
In this section, association among and gross domestic product and higher education in Pakistan is taken from the period of 1980 to 2018, which is based on statistical tests. Before applying the ARDL model, unit root test would be used to check the stationery of the variables. The result of the unit root test is mentioned below:
Unit Root Test Results Table (ADF)
Null Hypothesis: the variable has a unit root
..........................
Chapter 6 Conclusion
6.1 Conclusion
In this study it?s aimed to seek the long run relationship in Pakistan among higher education and economic growth from 1980 to 2018 by taking long term annual data. Co-integration approach of ARDL bound testing finds that in long run positive relation exists among higher education and Pakistan?s economic growth. Two econometric models have been used in this research. Stationery of all the variables is needed to be checked before finding the results of ARDL model. For this purpose ADF test is applied and results indicated that all variables are stationery at level and first difference.
The investigated variable of Model 1 shows that economic growth and examined variables (Gross fixed capital formation, higher education enrollments, Higher education expenditures, Exports) have long run relationship. First model estimated the higher education effect on GDP. Results found a positive relation among both variables. Other explanatory variables GFCF, HEExp, Exp are also effecting positively to economic growth of Pakistan with respect to higher education. Moreover, results of inflation and FDI are showing negative effect on economic growth with respect to higher education. These results make this study unique as compare to previous studies. These negative results are because of unpredictable economic policies by un-expert policies makers and high corruption in education sector.
reference(omitted)
