CHAPTER ONE
1. Introduction
In the modern world, there is mutual interdependence of the various national economies. Today it is hard to find the example of a closed economy. All economies of the world have become open. But the degree of openness varies from one country to another. Thus, in the modern world no country is completely self-sufficient. Self-sufficiency, in the sense used here, means the proportion of the goods and services consumed to their total output produced with in a country. But the degree of self-sufficiency varies from one country to another.Regional and international specialization cannot be left out since its so crucial to this subject for extremely important roles they play. Regional specialization means that various regions or areas in a country specialize themselves in the production of different products. International specialization means that different countries of the world specialize in producing different goods. Factors which determine regional specialization are more or less the same as those which determine international specialization. A country which produces surplus of a good, i.e produces more than its requirements, will export it to other countries in exchange for the surplus produces of those countries.
International trade is the exchange of goods and services between countries. Thistype of trade gives rise to a world economy, in which prices, or supply and demand is affected by global events. In most countries, such trade represents a significant share of gross domestic product (GDP). Trading globally gives consumers and countries the opportunity to be exposed to goods and services not available in their own countries. Ghana is a middle-income West African country which experienced impressive economic growth from 2005 to 2012. This growth has slowed significantly since 2013 in light of macro-economic challenges, such as high budget deficit and inflation, but has been remain positive due to the country?s stable democratic institutions and rich natural resources.
..........................
1.2 Problem Statement of the Study
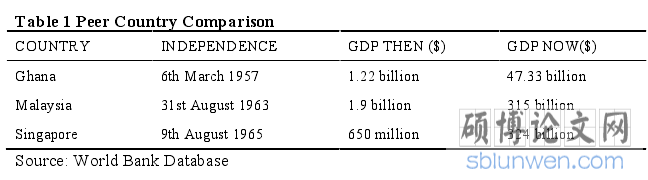
Table 1 and figure 1 below shows comparison of Ghana among her peers in the early 1960s. It depicts how well Malaysia and Singapore are doing so well while Ghana woefully lagging behind at tortoise pace. Ghana has not really benefited from international trade because growth has not been rapid and intensive though she is endowed with many natural resources. Perhaps there is something wrong with our approach toward international trade hence the need to investigate.
............................
CHAPTER TWO LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 A Brief Background to the Theory of Economic Growth
Economic growth, which basically refers to an increase in national output or income over time, traces its conceptual foundation to Adam Smith?s 1776 seminal publication The Wealth of Nations. Even though the book mainly concentrated on the division of labour, productivity and free markets, Smith managed to provide three major sources of growth in a dynamic economic model namely: growth in labour force and capital, improvements in productive efficiency, and promotion of foreign trade. Thus for Smith, capital accumulation is the decisive catalyst for economic growth (Harris, 1978).
David Ricardo (1817) improved on the above concept of economic growth (wealth accumulation) by adding technology to Smith?s production function which contained land, capital and labour force as the only sources of productivity growth. More importantly he argues that economic growth also emanates from foreign trade when countries produce and export goods and services, in which they have the best comparative advantage. However, the two differ in their view on the pace of productivity growth in that Smith?s framework posits accelerated growth while Ricardo postulates declining growth over time. Smith together with Ricardo and Thomas Malthus (1798) are considered to be the pioneers of the classical economic growth theory (Ibid).
Karl Marx (1872) looked at economic growth as emanating from the reinvestment of the society?s surplus value into the economy which in the end reproduces even more surplus value. The main inputs in this reproduction are labour, physical capital and technological produce (Sardadvar, 2011). During the Great Depression in the 1930s when the world economy was facing a severe recession, John Maynard Keynes (1936) argued that economic growth could be achieved through increasing money supply and expanding government spending. Thus boosting aggregate demand in the economy leads to economic growth and full employment (Ibid). However, it is Roy Harrod (1949) who is credited with influencing 20th century economists toseriously start thinking about economic growth. He is widely considered to be the ?founder? of modern economic growth. His model is discussed below.
..........................
2.2Economic Growth Theories in Relation to International Trade
2.2.1. Neoclassical Growth Theory
The traditional neoclassical model argues that economic growth results from increases in the quality and quantity of a country?s labour force, technology and the total capital stock. As An expansion in any of the above factors due to increasing returns to scale of inputs to outputs triggers an upsurge in the GDP levels over time,Todaro (2009) . Apart from the above factors the theory also envisages that some other factors such as foreign trade (exports and imports) have a significant role to play in growth. The model asserts that trade-induced GDP growth results from inter-country movements of foreign capital and investments from countries where there are lower interest rates and higher input costs to those with higher rates of return and lower input costs. In this case these capital movements can impact growth both from the export and import sides. For example, exportation of capital generates returns on investment for the exporting country while importing of foreign capital may increase the capital stock and boost productivity in the importing country, ceteris paribus. Thus open economies involved in international trade are more likely to experience more growth than closed or autarkical economies which have no external trading activities (Ghattak, 1978).
2.2.2 Solow Neoclassical Growth
Theory This theory is one of many extensions of the traditional neoclassical growth theory. According to Dasgupta (1998), Solow?s model basically follows the neoclassical economic tradition by analyzing economic growth (Y) as occurring through a production function containing factors such as labour (L), capital (K), and the level of technology (A) is assumed to be given. More importantly, Dasgupta notes that the model assumes diminishing marginal returns of the inputs to output as shown by the elasticities of labour (β) and capital (1-β) with respect to output.According to this theory, foreign trade has a part to play in attaining economic growth.Foreign trade as characterized by the importation of foreign technology and skills transfers also improves the effectiveness and efficiency of domestic labour and capital which enables a country to maximize its comparative advantage thereby allowing it to maximize its gains from trade which in the end increases the level of GDP (Gunter, Taylor and Yeldan 2005).
................................
CHAPTER THREE OVERVIEW OF INTERNATIONAL TRADE AND TRADE RELATED DEVELOPMENTS IN GHANA ................ 22
3.1 Trade Development in Ghana ...................................... 22
3.2 Ghana?s Export and Import Markets ....................................... 25
CHAPTER FOUR ................................. 44
METHODOLOGY ................................... 44
4.1Description of the Study Area .................................... 44
4.2 Research Design ......................................... 45
CHAPTER FIVE ......................................... 53
FINDINGS AND STATISTICAL INTERPRETATION ........................... 53
5.1 Diagnostic Tests ................................. 53
5.1.1 Test for Serial Correlation ........................... 53
5.1.2Test for Multicollinearity among the Explanatory Variables ........... 54
CHAPTER FIVE FINDINGS AND STATISTICAL INTERPRETATION
5.1 Diagnostic Tests
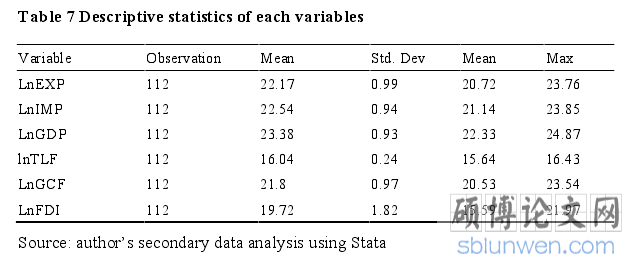
In order for the results of OLS method of estimation to be reliable, its assumptions must hold. To ensure this, the study employed the Breusch-Godfrey test for serial correlation of the residuals, the Breusch-Pagan test for heteroscedasticity and the Correlation Matrix for multicollinearity.Table 6 below show the descriptive statistics of each variables.
.................................
CHAPTER SIX CONCLUSION AND POLICY RECOMMENDATION
6.1 Exports-Related Policy Implications and Recommendations
As was shown in the study, the positive and statistically significant result for exports has important policy implications for the country?s economic growth and development agenda. Firstly, it shows that the ELG hypothesis strongly holds as was alluded to earlier on. Therefore, the Government of Ghana should continue with export-led economic growth and development strategies such as the Economic One District One Factory (1D1F) and Planting for Food and Jobs since there is strong empirical evidence in support of the export-led development agenda.
More importantly,Ghana needs to diversify her export basket if the export-led growth agenda is to be sustained. Ghana fails to maximize export revenues and suffers from export price volatilities because its export basket is still unrefined as shown by the country?s over-reliance on cocoa,timber,gold,crude exports. Also needs to embark on value-addition if the ELG agenda is to bear meaningful fruit. The government needs to invest in technologies that can help in processing its primary export commodities in order to boost its export quality and the revenues they can fetch. Alternatively, this can be done in partnership with foreign investors. As a way of promoting exports, the Government of Malawi should also consider providing subsidies to export-oriented producers especially smallholder farmers and small and medium scale enterprises (SMEs) who drive the economy. In addition, export producer prices should beincreased on the country?s major export commodities wspecially cocoa. These subsidies and high producer prices will incentivize smallholder farmers to continue with export production and consequently lead to more export revenue for the country.
Ghana also lacks adequate productive capacity to take full advantage of the multitude of international trading opportunities available in global markets.The deficiency in productive knowledge is exhibited through the presence of an unskilled labour force, insufficient technology and poor access to financial capital. This reduces Ghana?s export volumes through inefficient utilization of the country?s productive resources and thus leads to high opportunity cost in terms of export revenue.Therefore the government needs to invest heavily in acquiring modern technology and in skills development of the labour force. In addition to this, the state needs to provide easy access to financial capital to export-oriented industries more especially small and medium scale enterprises (SMEs).
reference(omitted)
