CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
The electricity sector in Pakistan is currently facing the formidable challenges of an insufficient installed capacity, a suboptimal infrastructure, circular debt and revenue shortage. All of these problems hamper socioeconomic activities. Meanwhile energy is an important mean of economic growth and other sectors of economy. The energy shortage is the difference between demand and supply of energy. Pakistan is endowed with energy crisis since beginning. This study is an endeavor to shed some light on economic growth and energy usage.
Energy is considered to have significant impact on manufacturing sector production ( Stern, 1993; Stern, 2000; Oh and Lee, 2004a; Oh and Lee, 2004b; Ghali and El-Sakka, 2004; Beaudreau, 2005), economic growth (Cleveland et al. 1984; Shiu and Lam, 2004; Liddle, 2013; Meng et al., 2015; Zheng & Walsh, 2019), engineer production (Beaudreau , 1995), human development (Arto et al., 2016; Ferguson et al., 1997; Mattick and Allenby, 2010), CO2 emissions (Zhao et al. 2013; Kan et al. 2012; Qureshi et al. 2015; He′roux et al. 2015; Liao et al. 2016), foreign direct investment (Omri and Kahouli, 2014; Zaman et al., 2012; Tang, 2009; Sadorsky, 2009; Chandran et al., 2010), employment & job creation ((Observ'ER, 2010; Gearthblog, 2009).
Regarding, the channels through with energy can affect the economic growth is its contribution in manufacturing and other sectors of the economy. Without the abundance of energy, a country cannot achieve sustainable growth performance. Its importance in the manufacturing process has been acknowledged by some influential studies ( Stern, 1993; Stern, 2000; Oh and Lee, 2004a; Oh and Lee, 2004b; Ghali and El-Sakka, 2004; Beaudreau, 2005).
.........................
CHAPTER 2 Overview of energy crisis and economic growth in Pakistan
There is acute shortage of energy in Pakistan. In winters there is no gas and in summer there is no electricity. The previous governments did not bring some good reforms to solve the problem. Mostly, the power cut off remains for several hours in a day. Pakistan energy network is struggling hard to fulfill the country power requirements. The shortage of energy badly affects the economic growth, jobs, employment, and productivity.
The rising prices of electricity and other energy resources also affect the household and industrial sector productivity. Most often it has been seen that people protest against the government. Many small and medium businesses mainly rely on the supply of electricity. The power cut may outperform their activities and ultimately cut down production and job loss. The power outages have been ongoing for several years worsening under the last government that was unable to curb the evil of load-shedding. This ultimately crippled the businesses and industries particularly those that cannot afford their own generators.
The energy shortage also affects the education sector of Pakistan which is considered to be a backbone of modern economic system. The lab work, internet and computer system working disturb during the power cut down. Similarly, the routine as well as sudden failure of power may result in data and work loss. Similarly, students cannot concentrate in the absence of power.
According to the Zhag & Fan (2019) up to 50 million Pakistanis are lacking accesses to grid electricity. Pakistan is 115 among the 137 nations to have access to electricity, similarly in 2015 the distortions in power sector cost Pakistan 7% of its GDP which amounting 18 billion dollars a year.1 The report sheds new light by analyzing distortions in the entire power supply cycle all the way from upstream fuel supply to power generation, transmission, distribution, and to consumers. Problems begin upstream when gas under pricing encourages waste and lower production. More than 14% gas is lost in transmission and distribution due to lack of pipeline maintenance and theft which result in gas shortages and power outages. Public power plants use 20% more gas per unit of electricity produced than private power plants. Faulty metering, poor infrastructure and theft cause the loss of almost one fifth of generated electricity.
.............................
CHAPTER 3 Theoretical framework of the study .................................. 7
CHAPTER 4 Literature review ...................................... 9
CHAPTER 5 Data & Methodology ......................................... 16
CHAPTER 5 Data & Methodology
The study is based on time series annual data. GDP growth is the derived for World Bank database. It is annual growth rate in percentage. Keeping in view the past literature regarding the energy and growth nexus, we use energy infrastructure as a proxy for energy shortages and consumption. Therefore, we rely on the data by Donaubauer, J., Meyer, B. and Nunnenkamp, P. (2015); the authors used unobserved component model (UCM) to construct the energy infrastructure data and used electric power consumption and production (both variables are measured in per capita terms). Moreover, to measure the reliability and quality of the national electrical power supply the authors used data on electric power transmission and distribution losses (as percentage of output).
Figures 1 and Figure 2 plot the energy infrastructure index and economic growth. The graphs suggest positive relation between these variables. It suggest to energy infrastructure is an important factor in the economic growth. Reverse is also true. GDP growth also affect energy infrastructure.
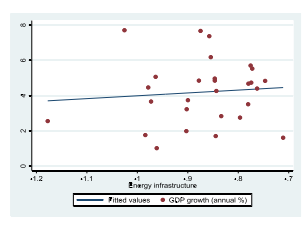
............................
Conclusion
Energy play an important role for sustainable development and economic growth. Since its independence, Pakistan is facing acute energy crisis. Pakistan mainly relies on the import of energy resources like oil. Pakistan is producing natural gas; however, its needs are more than its production which cause low productivity, job loss, and economic growth. My study is an endeavor to identify the impact of energy infrastructure on economic growth of Pakistan. I apply ARDL model to explore the relationship between these variables. Our findings report that energy plays weakly positive role in economic growth. I control for other variables like ICT, institutional quality, foreign direct investment, trade openness, domestic investment, and human capital which yield coefficients according to the prior expectation of economic theory.
The results of the study show that energy infrastructure plays positive role which are consistent to the results of previous studies. Similarly, institutional quality also found to have a significant and positive impact on economic growth. Due to its spillover effect and forward/ backward linkages, foreign direct investment in considered to have a positive and significant impact on economic growth which is proved by the findings of the study. Domestic investment is found to have a significant and positive impact on economic growth of Pakistan.
reference(omitted)
