Chapter One Introduction
1.1 Research Background
Speech is important for people to learn languages and communicate in different occasions. A good speech learning is one of the most important processes in the English learning. Whether students have a good grasp of pronunciation and intonation, it has a close relationship with their listening ability, reading, understanding and appreciation of literary works. The famous British linguists Gimson (1989) also said that if one wants to master a second language and become elite of this language, 50% to 90% of grammar, 1% of vocabulary and 100% of this language’s speech are to be attained. Language, coming down to it, is a tool of social communication, a combination of vocabulary and grammar. Grammar indicates the organization law of language. It gives language the institutional system, and the information transmitted is first expressed through the phonetic and phonological system. Therefore, speech is the material medium of semantics, which is also the basis for the existence and development of language. If students can master the speech well, it will boost their confidence in learning English and increase their enthusiasm for learning English.
Every language has its own voice system and laws of pronunciation and their own features have an unavoidable influence on speech learning. If two languages belong to different languages families, there would be many differences in all aspects. The Chinese language belongs to Sino-Tibetan language family while English to Indo-European language family. The differences between two languages in phonetics are distinctive: The Chinese literal system is ideogram based, which could express meaning and has a certain phonetic function at the same time, while the English literal system is a typical alphabetic writing (Shao, 2001). Non-equivalence of the phonology between first language and second language can make second language learners transfer some phonemes of their first language directly or indirectly to the target language by mistake, deviating from the original pattern of second language speech (Flege, 1987; Best, 1995; Kuhl and Iverson, 1995) and causing perceptual slowness, production error and communication failure (Munro and Derwing, 1995; Escudero, 2005). Chinese language usually imposes influences on English pronunciation of Chinese people in different degrees. Thereby, the advanced English speakers could feel an obvious accent in some Chinese English speakers.
.........................
1.2 Purpose and Significance of the Research
This research aims to study the situation of English diphthong perception and production of Changchun English learners in the northeast dialect area, and the relationship between them. Through the perceptual experiment, where exact diphthongs are marked by subject students in multiple choices, the learner's correct rate of diphthong perception is collected and calculated. And then the author will conduct the acoustic analysis of diphthong production by the same group after the perception test. The learner's specific sound production is under collection. Through the Combination of the results of two tests, it is easy to find where problems lie. With the application of statistical analysis method, the relationship between perception and production is founded. The specific research questions are as follows:
(1) To what extent do Changchun English learners perceive English diphthongs correctly?
(2) What are the features of the production of English diphthongs by Changchun English learners?
(3) To what extent does the subjects’ perception of English diphthongs correlate with their production?
In practical English teaching process, Chinese English learners may not speak English in a fluent speed, though the English speech has gained some attention, as vowels usually bring big troubles to Chinese students (Zheng et al., 2012). Zhang (2002) also claimed, “Vowels often pose great difficulties for Chinese students”. Diphthongs are a vital part within vowels while relevant studies about them are not sufficient in quantity. Through the phonetic experiment analysis, the author aims to research the diphthongs production and perception situations of English learners in Changchun city, Jilin Province, located in Northeast area, China, and trys to find the differences in acoustic features between them and native speakers as well as the relationship between diphthongs perception and production.
......................
Chapter Two Literature Review
2.1 The Key Terms
This section explains some terms related to the research which helps facilitate the development of the thesis, which includes English diphthongs, Northeast dialect and Mandarin.
2.1.1 English Diphthongs
Vowel and consonant are two basic concepts of phonetics, known as phonemes, on which the classification and description of the quality of sound in phonetics are based (Lin and Wang, 2013). Generally speaking, almost all languages have at least one vowel in its phonological system. As it has a great advantage in the length and intensity of syllables, it has been considered the focus of studies by phonologists and speech engineers, and posed difficulties for learners, too.
Cen (2013) claims that as for English, there are four types of vowel classification: (1) closed vowels, semi-closed vowels, semi-open vowels and open vowels (2) front vowels, central vowels and back vowels (3) round lip vowels and non-round lip vowels (4) nasal vowels and nasalized vowels. As a kind of compound vowels, diphthongs belong to the combination and composition of sounds (which also includes fricative and compound consonant), not to the classification of vowels.
According to Bao and Lin (2014), compound vowels can be divided into two categories in terms of its quality: true compound vowels and false compound vowels. True compound vowels refer to two target vowels with long stable segments on the sound spectrogram, but the transition between the two target values of vowels is relatively short. In response to this, there are often two peaks on its intensity curve, or although only one peak exits, there is a quite long continuation after that. False compound vowels have two target positions. According to their differences in length and intensity, they can be divided into two types: front-accent diphthong and back-accent diphthong-- according to this division, most of the diphthongs in English are the front-accent diphthongs. From the perspective of the formant pattern of vowels, they are in a sliding state, with few stable segments. Only the latter part of vowel in the back-accent diphthongs may have stable segments.
.........................
2.2 Relevant Studies
2.2.1 Relevant Studies on Perception and Production of Diphthongs Abroad
In foreign countries, scholars' researches on the perception and production of English vowels by Chinese native speakers are mostly appeared in the 1990s and the early 21st century. All of these studies aim to find out the difficulty of perceptual and producing English vowels under the influence of the Chinese phonetic system to verify SLM and CAH.
Ma (1995) investigated the production of English five front vowels and diphthongs (beat, bit, bait, bet, bat) in the carrier sentence, compared with the production by American native speakers, using a sound spectrograph to analyze frequencies.
Wang (1997) conducted perceptual and production tests on fifteen native Mandarin speakers from Beijing who had been living in Canada between 0.5 and 6 years, testing the isolated English vowels in a carrier sentence. The results of production and perceptual showed that the vowels that have Mandarin counterpart were performed better than those lacking obvious counterpart. But the relation between production and perceptual are convoluted. These results also examined the usefulness of two hypotheses in predicting problems faced by Mandarin speakers learning the English vowel system: the Contrastive Analysis Hypothesis and the Speech Learning Model.

........................
Chapter Three The Theoretical Framework ......................................... 20
3.1 Language Transfer ................................. 20
3.2 Contrastive Analysis Hypothesis ............................ 21
Chapter Four Research Methodology ............................... 24
4.1 Research Questions ............................. 24
4.2 Research Design .................................. 24
Chapter Five Results and Analysis .................................. 29
5.1 Results and Analysis of Perception Experiments .............................. 29
5.1.1 The Results of Perception Experiments by Advanced Learners .............. 29
5.1.2 The Results of Perception Experiments by Intermediate Learners ........... 31
Chapter Five Results and Analysis
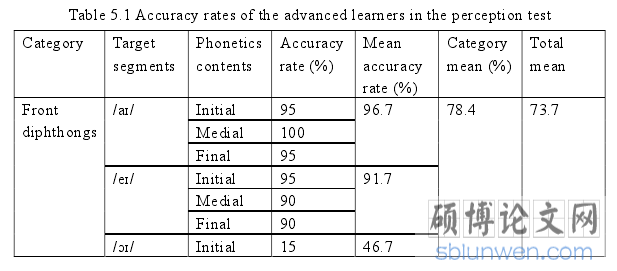
5.1 Results and Analysis of Perception Experiments Forty students are divided into two groups, intermediate learners and advanced learners according to their CET 4 scores. The one whose scores is over 425 is intermediate learner and the one over 550 advanced learner. They are told to listen to the 69 (23*3) tokens of all eight English diphthongs and to do the multiple choice so that their performance could be collected and analyzed. The correct identification rate is calculated individually and the total accuracy rate of each diphthong and of each category are averaged into mean identification rates under the help of Miscroft Excel. The listening file, which is used as the standard sound for the perception adopted the synthetic pronunciation of carrier words based on standard American pronunciation. The relevant data is extracted through Praat and its scripts.
The accuracy rates of all the 69 tokens coming from the both groups in the perception experiment were showed in bellow.
5.1.1 The Results of Perception Experiments by Advanced Learners
........................
Chapter Six Conclusion
6.1 Major Findings
The present research explored Changchun English learners` production and perception of eight English diphthongs. And the major findings can be illustrated as follows:
1. According to the Pearson Analysis and Linear Analysis, the results show that the perception and production of both Changchun advanced and intermediate learners have a positive correlation (r=0.472, Sig.=0.238; r=0.753, Sig.=0.051) with each other. Meanwhile, the correct perception rate is higher than that of the production in both groups. However, there are three spots scattered away from the line in advanced group, and two spots away from the line in the intermediate group. From the linear diagram of their relationship, the perception by advanced learners has a moderate positive correlation to the production while relationship between the perception and the production in the intermediate group is strong positive. This implies that good perception acquisition can sometimes stand for good production accuracy for advanced learners. And for the intermediate learners, good perception acquisition can represent good production accuracy in Changchun.
The significance of this thesis is mainly reflected in theory and practice two aspects. From the theoretical perspective, this thesis can provide strong empirical data for the relevant second language acquisition theory. A lot of researches have been done on L2 speech acquisition since the end of the 20th century. Many Chinese researchers (Liu, 1996; Lin, Han, Tan, etc., 1999; Liu, 2002; Shi, 2003) have used descriptive methods to study L2 speech acquisition. But there are few L2 perception and output experiments influenced by L1 for the speech studies. In addition, in the speech experiment, this thesis studies two groups subjects, advanced learners and intermediate learners, to further observe the difference existed between the perception and production. Next, most researches on the perception and production of English vowels are focused on contrastive sounds (Wu, Yang, 2016; Zhang, 2016) or some single tones (Zhou, Shao, Chen, 2010; Jin, 2011; Feng, 2015; Xue, 2018), while the number of researches on perception and production of English diphthongs is relatively small, and the number of experimental researches on perception and production of eight English diphthongs in Northeast dialect area is zero. Last but not the least, this study can confirm Language Transfer theory, Contrastive Analysis Hypothesis (Lado, 1957) and Speech Learning Model (Flege, 1987, 1993) to some extent.
reference(omitted)
