本文是一篇国际贸易论文,本研究总体结果表明,国际贸易对这九个非洲国家而言是一个主要问题。未来的研究应着眼于研究这九个国家在实施促进国际贸易和经济增长方面政策计划过程中政府的确切作用,还可以进一步选取其他变量如市场规模、经济自由和专利作为中介变量,研究国际贸易对经济增长的影响。
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 Research background
International trade is the exchange of goods and services between countries. Total trade equals exports plus imports. The Oxford Advanced Learner dictionary defines trade as "the activity of buying and selling or exchanging goods and services" (Rai & Purvashree, 2015). According to Investopedia, global trade exposes consumers and countries to goods and services that are not available or would be more expensive in their home countries. Some argue, however, that foreign trade can be detrimental to smaller countries, putting them at a significant disadvantage on the global stage.
Economic growth is a measure of an increase in real per capital income of a country which can be sustained over a long period of time (Clunies, 2009). East Africa retained its lead as the continent's fastest-growing region in 2019, with average growth estimated at 5.0 percent; North Africa was second, at 4.1 percent; and West Africa's growth increased to 3.7 percent in 2019, up from 3.4 percent the previous year. Central Africa grew at a 3.2 percent annual rate in 2019, up from 2.7 percent in 2018, while Southern Africa's growth slowed significantly over the same period, from 1.2 percent to 0.7 percent, hampered by cyclones Idai and Kenneth. Central and West Africa, on the other hand, had the worst growth rates of 0.8 percent and 0.4 percent, respectively. The poor performance of Equatorial Guinea and Chad slowed Central African growth. West Africa, on the other hand, was dragged down by Nigeria's economic recession (World Bank, 2018).
Based on the foregoing, this study seeks to empirically examine the impact of international trade on economic growth in East African countries using panel data from 1999 to 2018, and to make appropriate policy recommendations based on the study's findings.
..............................
1.2 Research Significance
This research will be the knowledge spillovers to the academic literature of other future research and to other parts of the economy of East African Countries (Burundi, Djibouti, Ethiopia, Kenya, Madagascar, Rwanda, Somalia, Tanzania and Uganda). The study will also significantly fill the gap in determining the impact of International Trade on economic growth in East African Countries with a precise attention on absorptive capability factors. There has never been a country that has grown without the useful tool of trade; however, the importance of international trade to economic growth is heavily dependent on the conditions under which it operates and the purpose it serves. The importance of international trade stems from the fact that no country can produce all resources in terms of goods and services that its population needs for their use and consumption, owing to resource differences and constraints. As a result, it is concluded that a trade relationship between countries is essential, because revenue generated from commodity exports can be used to import commodities that cannot be manufactured domestically. Innovation is one of a more extensive system; innovation must be seen as item or interaction, yet additionally interrelationship between innovation and trade and the relationship between innovation and economic growth must be recognized.
国际贸易论文怎么写
............................
CHAPTER 2 THEORETICAL CONCEPTS AND RELATIONS
2.1 Some Theories of International Trade
In this section we are going to find a brief overview of related international trade theories and the possible relations between trade and growth. These international trade theories include: Heckscher-Ohlin theory; product cycle theory and Linder’s theory of representative demand; cumulative causation theory; endogenous growth theory; and new trade theory. International trade exerts considerable effect on economic growth. The classical and neo-classical economists attached importance to the role international trade plays in a nation’s development and regarded it as an “engine of economic growth”.
2.1.1 Heckscher-Ohlin Factor Endowment Theory
Between the 1920s and the early 1980s, the Heckscher-Ohlin theory (named after its original formulation by two Swedish economists, Eli Heckscher and his student Bertil Ohlin) dominated studies of international trade. It states that a country's exports are determined by its resource endowment, whether it is capital- or labor-abundant. If capital is plentiful, it will produce and export capital-intensive goods at a lower cost than the other country. Similarly, a labor-abundant country will produce and export labor-intensive goods at a lower cost than the other (Lam, 2015).
And Lam (2015) continue to explain that it is worth noting that the Ricardian and Heckscher-Ohlin models differ in that the former assumes that production technologies differ across countries, whereas the latter assumes that production technologies are the same. Furthermore, the Heckscher-Ohlin model assumes that there are no differences in aggregate preferences across countries. The only difference is that different countries have different resource endowments, and this significant difference is enough to cause a different production possibility frontier in the two countries, resulting in different equilibrium price ratios in an autarky.
...................................
2.2 Some theories about innovation
The Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) provides basic definitions and types of innovation (sometimes referred to as "shapes" or "typology" of innovation) in a series of manuals. The Oslo Manual is the most recent revision of these manuals, and it defines innovation as "the implementation of a new or significantly improved product (good or service), or process, a new marketing method, or a new organizational method in business practices, workplace organization, or external relations"(OECD/Eurostat, 2018). Here we have some types or kind of innovation, Technological innovation, commercial innovation, political innovation and organizational innovation.
2.2.1 Technological innovation and commercial innovation
According to the OECD, technological innovation is described as a new or improved product or process with technological characteristics that are significantly different from those previously available. New technologies (product innovations) or procedures in use (process innovations) that have been brought to market are examples of technical product innovations that have been implemented. A product or method is deemed innovative if it provides specific benefits to the company in question; these benefits do not have to be novel to other businesses or the industry.
Many people mistakenly believe that innovation is synonymous with technological innovation. This is taken for granted in the literature. Studies on technological innovation frequently use the term "innovation," despite the fact that they are primarily concerned with technological innovation. However, etymologically and historically, the concept of innovation is much broader (Benoit, 2008). While the concept of invention came to be associated with discovery in science (Branigan, 1981) and imagination in literature and the visual arts (Hausman and Engell, 1982; Mason, 2017), it gradually and increasingly came to be associated with mechanical or technological invention, first and foremost in crafts and arts such as architecture, navigation, metallurgy, and the military. The term invention applied early in the Renaissance to ingenious things like "machines, devices, engines, methods," which developed the entire literature (Lightsey and Long, 2003; C. S. Smith et al., 1971) which subsequently became a category for the word technology.
................................
CHAPTER 3 DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICAL ANALYSIS OF THE INTERNATIONAL TRADE AND ECONOMIC GROWTH IN EAST AFRICAN COUNTRIES .............. 26
3.1 International Trade’s historical development in East African Countries ........................... 26
3.2 Graphical representation of trade figures of East African countries. ................................. 29
CHAPTER 4 EMPIRICAL RESEARCH ON THE EFFECT OF INTERNATIONAL TRADE ON ECONOMIC GROWTH IN EAST AFRICAN COUNTRIES .......................... 42
4.1 Methodology ..................................... 42
4.1.1 Data source, variable selection, model selection and variables description................ 42
4.1.2 Panel data analysis .................... 45
CHAPTER 5 THE MEDIATION EFFECT OF INNOVATION ON THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN INTERNATIONAL TRADE AND ECONOMIC GROWTH ................................. 62
5.1 Construction of mediating Model ........................... 62
5.2 The unit root ..................................... 64
CHAPTER 5 THE MEDIATION EFFECT OF INNOVATION ON THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN INTERNATIONAL TRADE AND ECONOMIC GROWTH
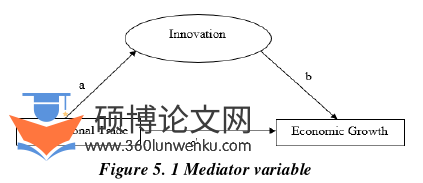
5.1 Construction of mediating Model
The model or framework is the fundamental establishment on which the mediation action was developed. This framework was carried out to give the overall thought regarding to the mediation. Trade decisions have taken a gander at how nations react to the economic accords and treatment they get from different nations in the light of the correspondence hypothesis. The most among these reactions incorporate yet not restricted to nations' obligation to each other and the goal to stop or keep having exchange relations with others. The exploration structure was drawn dependent on the traditional and standard methods of mediation. The model was consequently 5.1 Construction of mediating Model The model or framework is the fundamental establishment on which the mediation action was developed. This framework was carried out to give the overall thought regarding to the mediation. Trade decisions have taken a gander at how nations react to the economic accords and treatment they get from different nations in the light of the correspondence hypothesis. The most among these reactions incorporate yet not restricted to nations' obligation to each other and the goal to stop or keep having exchange relations with others. The exploration structure was drawn dependent on the traditional and standard methods of mediation. The model was consequently
国际贸易论文参考
In the wake of running the unit root test, the Standard Approach will be utilized to evaluate the mediating impacts between the factors. The hypothesis begins with a noticed relationship between an independent factor ????, and dependent variable ????. At that point, the hypothesis contends that ???? probably won't cause ????. Or maybe, ???? influences another variable ????. ???? thusly, influence ????. In this way, ???? intervenes the relationship among ???? and ????.
.................................
CHAPTER 6 CONCLUSION, RECOMMENDATIONS AND LIMITATIONS
6.1 Conclusion
The study examined whether or not international trade can have an impact on economic growth of nine Eastern Africa countries. It also investigated whether GDP had significantly long run relationship between the other variables. The analyses were made using panel data analysis and the granger causality test to first assess the effects of international trade on GDP, investigate if there exists a long-run relationship between the dependent and independent variables and lastly to understand the bidirectional or unidirectional casual trend between the factors. The study used secondary panel dataset spanning the period of 1999 to 2018.
The findings of the research will be explained based on the research outcome.
(1) The result of the study brought to light the massive effect of international trade and FDI on Economic growth and advancement.
The results of the study show that the positive effect of international trade on economic growth is significant. Again, the result of the study provided evidence that international trade has a significant positive influence on FDI. The study however brought to light that inflation has a significant negative influence on Economic growth and international trade. The research can therefore conclude that international trade determines Economic growth and also if the other variables stay positive then any improvement goes into strengthening Economic growth of these countries in that regard. It is difficult for an economy that does not do any form of international trade to be committed in improving Economic development and FDI figures.
reference(omitted)
