本文是一篇国际贸易论文,本论文探讨了马来西亚出口对苏库克发行规模的影响,重点分析了两者在短期和长期的动态变化。作为一种重要的伊斯兰金融工具,苏库克在马来西亚资本市场中扮演着关键角色,为基础设施建设和贸易相关投资提供融资支持。
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1 Research Background
With the proliferation of fintech and the increasing use of blockchain technology in Sukuk issuance, understanding how exports impact Sukuk issuance becomes even more crucial. The growing interconnectedness of financial markets and international trade necessitates an examination of the dynamic and potentially symbiotic relationship between these two sectors. This research aims to bridge this knowledge gap by analyzing how Malaysia's export performance influences its Sukuk issuance across different time periods and economic conditions, particularly during periods of global financial uncertainty.
1.1.1 Overview of Sukuk Issuance in Malaysia
Malaysia has long been regarded as a global leader in the Islamic finance industry, with Sukuk serving as one of the primary instruments that have propelled the country's reputation. Sukuk, often referred to as Islamic bonds, differs from conventional bonds by adhering to Shariah principles, prohibiting riba (interest) and ensuring that investments are backed by tangible assets. Since the early 2000s, Malaysia has pioneered the development of the Sukuk market, accounting for more than half of global Sukuk issuances as of 2020 (IFSB, 2020). Malaysia's robust regulatory framework, strong financial infrastructure, and the active role of government and Islamic financial institutions have fostered this rapid growth.
国际贸易论文怎么写
.........................
1.2 Significance of Study
The significance of this study lies in its potential to provide crucial insights into the relationship between Malaysia's export performance and Sukuk issuance. This relationship has far-reaching implications for policymakers, investors, and market participants in Malaysia and globally. Understanding the dynamics between Malaysia's exports and Sukuk issuance can help shape better monetary and fiscal policies, allowing the country to capitalize on its export-led growth while maintaining a strong and sustainable Islamic finance ecosystem.
Moreover, this study comes at a time when the global economic landscape is shifting rapidly due to factors such as technological advancements, geopolitical tensions, and the COVID-19 pandemic. The latter, in particular, disrupted global supply chains and dampened export activities worldwide. Given that Sukuk has often been utilized as a financing tool during periods of economic distress (Mzoughi, Ben Amar, Belaid, & Guesmi, 2022), understanding the relationship between export shocks and Sukuk issuance during crises like the pandemic offers valuable lessons for future financial planning.
This research also aims to fill a gap in the existing literature. While previous studies have explored the growth of Sukuk markets and their importance in Islamic finance (Jobst et al., 2008; Ahmad & Radzi, 2011; Azmat et al., 2014), few have focused explicitly on how external trade, particularly export performance, influences Sukuk issuance. The study of Malaysia’s exports in relation to sukuk issuance provides strategic insights into how Islamic financial instruments are leveraged to support economic growth and trade in Malaysia.
................................
Chapter 2. Literature Review
2.1 Islamic Finance and Islamic Banking Researches in China
Islamic finance has become an area of increasing interest in China, the research on Islamic finance and banking in China has seen a gradual but significant development over the years, reflecting both the growing interest in Islamic financial principles and the increasing relevance of its potential to support the country's economic strategies, such as the development of inland economies and participation in the Belt and Road Initiative. This sub-chapter literature review synthesizes key points from recent Chinese-language research articles, highlighting key trends and developments from foundational studies to more recent explorations of the potential integration of Islamic finance within China's economic framework.
The early studies on Islamic finance in China focused primarily on understanding the foundational principles and characteristics that differentiate Islamic finance from conventional finance. Ba, Liu, and Cui (2009) studied into the essential characteristics of Islamic finance that differentiate it from conventional financial systems. They realized the ethical principles that underlie Islamic finance, including the prohibition of riba and the requirement for all financial transactions to be asset-backed. This work is significant in that it sets the theoretical foundation for understanding how Islamic financial instruments could function in a non-Islamic financial system like China's. This research underscores the potential of Islamic finance to offer a more stable and ethically grounded financial system, particularly important as China seeks to diversify its financial services and appeal to international Muslim investors.
.........................
2.2 Global Researches on Islamic Finance, Islamic Banking and Sukuk in Malaysia
Islamic finance, rooted in Shariah principles, has shown substantial global growth, establishing itself as an ethical and resilient component within the international financial system. At the center of Islamic finance is sukuk, or Islamic bonds, which serve as crucial tools for capital mobilization in compliance with Islamic principles. A key strength of Islamic finance lies in its stability during economic downturns, attributed to its asset-backed structure and risk-sharing mechanisms. Beck, Demirgüç-Kunt, and Merrouche (2018) demonstrate that these characteristics contribute to lower volatility, particularly compared to conventional finance. Their findings underscore the potential of Islamic finance as a stabilizing force, especially during financial crises, by avoiding speculative practices and excessive risk-taking.
2.2 Global Researches on Islamic Finance, Islamic Banking and Sukuk in Malaysia Islamic finance, rooted in Shariah principles, has shown substantial global growth, establishing itself as an ethical and resilient component within the international financial system. At the center of Islamic finance is sukuk, or Islamic bonds, which serve as crucial tools for capital mobilization in compliance with Islamic principles. A key strength of Islamic finance lies in its stability during economic downturns, attributed to its asset-backed structure and risk-sharing mechanisms. Beck, Demirgüç-Kunt, and Merrouche (2018) demonstrate that these characteristics contribute to lower volatility, particularly compared to conventional finance. Their findings underscore the potential of Islamic finance as a stabilizing force, especially during financial crises, by avoiding speculative practices and excessive risk-taking.
..............................
Chapter 3. Theoretical Framework ....................... 15
3.1 Export-Led Growth Hypothesis (ELGH) ................................ 15
3.1.1 Key Mechanisms of Export-Led Growth Hypothesis ..................... 15
3.1.2 Export-Led Growth Hypothesis (ELGH) Model ................................. 15
Chapter 4. Methodology ................................... 26
4.1 Data Collection ....................................... 26
4.2 Empirical Framework: Vector Autoregression (VAR) Model ........................... 26
4.3 Dependent and Independent Variables ................................... 28
Chapter 5. Empirical Analysis ..................................... 30
5.1 Empirical Model ........................................... 30
5.2 Descriptive Analysis ................................................ 30
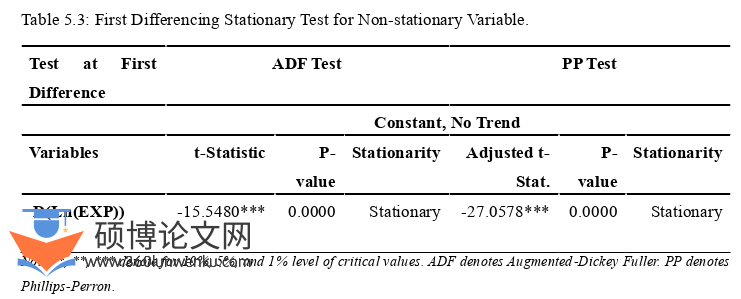
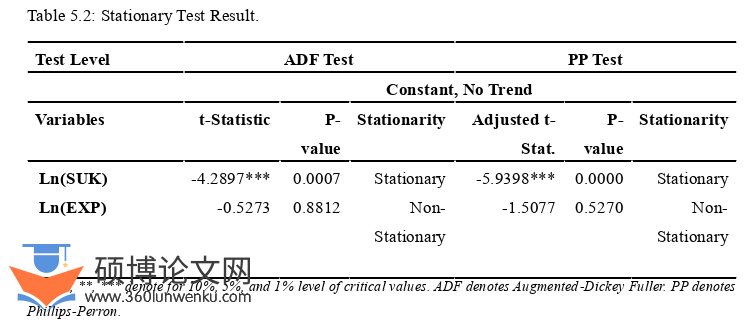
5.3 Stationary Test ....................................... 31
Chapter 5. Empirical Analysis
5.1 Empirical Model
This empirical analysis investigates the relationship between Malaysia's exports and Sukuk issuance using time-series data. The VAR model is particularly useful when examining the dynamic interplay between Sukuk issuance and exports, as both variables exhibit significant interactions and feedback loops over time. The suitability of VAR lies in its ability to model complex economic interactions using multiple time-series variables in a system of equations.
In this study, we employ the VAR model to analyze the relationship between Malaysia's Sukuk issuance (dependent variable) and exports (independent variable). The model captures how these variables influence each other both contemporaneously and over time. The VAR model for p lags in this study can be written as:
????????(????????????)????=????0+∑????????????????(????????????)????−????????????=1+∑????????????????(????????????)????−????????????=1+????1???? (5.1)
????????(????????????)????=????0+∑????????????????(????????????)????−????????????=1+∑????????????????(????????????)????−????????????=1+????2???? (5.2)
Where, ????????(????????????)???? the total Sukuk issuance in Malaysia at time t, ????????(????????????)????represents Malaysia’s total exports at time t, ????0 and ????0 are constants, ????????, ????????, ????????, ???????? are the coefficients to be estimated, ????1???? and ????2???? are the error terms.
国际贸易论文参考
.........................
Chapter 6. Conclusion and Policy Implications
6.1 Empirical Results supported Conclusion
The empirical analysis revealed a long-term positive relationship between exports and Sukuk issuance, meaning that an increase in exports tends to increase the issuance of Sukuk over time. The findings provide empirical evidence that aligns with two prominent economic theories: Endogenous Growth Theory and the Exports-Led Growth Hypothesis.
This outcome aligns with Endogenous Growth Theory, which posits that internal factors, such as technological innovation and capital accumulation, drive long-term economic growth. In Malaysia, Sukuk issuance displays momentum, with both the first and second lags showing positive and significant effects. This demonstrate that rising exports prompt greater reliance on Sukuk as a financing tool. This relationship aligns with the principles of Endogenous Growth Theory, where internal economic activities, such as export expansion, drive capital accumulation and financial growth. By channelling funds into development and infrastructure projects, especially in export-driven sectors, Sukuk issuance not only supports but amplifies Malaysia's economic expansion, enhancing the country’s capacity for sustained growth through robust, export-oriented financing.
The Export-Led Growth Hypothesis (ELGH) also provides a relevant framework for interpreting these results. ELGH suggests that export growth is a key driver of economic expansion, increased exports will fuel economic growth by creating demand, generating foreign exchange, and attracting investments. The empirical findings reinforce this hypothesis by showing that higher export performance generates the need for Sukuk issuance, particularly in the long term. The connection between exports and Sukuk supports the argument that trade and financial markets in Malaysia are closely integrated. Sukuk issuance can finance productive investments, which may boost future exports, with Sukuk serving as a financing mechanism to bolster the nation’s export-led growth strategy.
reference(omitted)
