Chapter 1 Introduction
1.1 Research Background
The 21st century is regarded as a knowledge-based era as well as an “information explosion”. Generally speaking, it is of great importance to think critically due to the skyrocketing development in such an information age. People have reached a widespread consensus that CT is among the list of five important skills for future citizens to develop (LIU, 2000). Therefore critical thinking has become one of the most important abilities and it is also of great value for school education. Strengthening the cultivation of critical thinking is of great significance in fostering students’ ability and personality as well as the improvement of the innovative exploration ability of the whole society.
Therefore how to improve students’ CT has been the hot spot of education reform since the early 20th century. Brown (2004) points out that the English curriculum should not only focus on the language knowledge, but also consider the development of critical thinking. Davidson (1998) also emphasizes the importance of critical thinking in foreign language teaching and advocates its integration into regular foreign language teaching. Ministry of Education changes the aim of teaching from the comprehensive language ability to English discipline core literary. It includes language competence, culture consciousness, thinking quality and learning ability. It is the first time that the thinking quality has been listed explicitly as one of the elements of the core quality of English subject. It enhances the educational values. Teachers and students should be free from the inefficient pedagogy which focuses on vocabulary and grammar. Students can develop the language knowledge as well as the expression competence and critical thinking skills.
............................
1.2 Purposes of the Study
The purpose of the current study is to explore the current situation of teachers cultivating students' critical thinking in English classroom on the basis of dialogism theoretical framework and by Newman’s critical thinking coding schema to do a quantitative and qualitative analysis of the critical thinking activities in English classroom discourse. Thus, the first aim of the study is to find out the overall level of students’ critical thinking in English class. And the second object is to let teacher know the emergence of applying CT in their class and give them some advice to enhance students’ CT.
In consideration of the above aims, the following research questions are discussed in the present study:
Question 1: what is the overall level of students’ critical thinking? (a) The level of students’ critical thinking in each class (b) The depth of students’ critical thinking in ten indicators Question 2: What’s the influence of the amount of students’ discourse on critical thinking?
..............................
Chapter 2 Literature Review
2.1 Classroom Discourse
According to the dictionary, discourse means written or spoken communication or debate, a formal discussion of a topic in speech or writing or a connected series of utterances; a text or conversation.
2.1.1 The Definition of Classroom Discourse
Classroom-based research studies define discourse as the oral interaction between teachers and students or among students themselves in classroom context. Some researchers wonder to know how learners set up relationships with their classmates in classroom contexts by talk-in-interaction (Hellermann, 2007, 2008). Gee defines discourse as an instrument for the social construction of experience (Gee, 2004). Although different researchers have different opinions, they all agree that classroom discourse is a tool to establish relationship between students and teacher.
Bernstein defines the discourse at issue as pedagogic, he takes into account two subjects in classroom learning: persons who take part in the construction of the discourse and who are influenced by it (Bernstein, 1997).
That is to say he both considers students and the teacher. And he thinks it is quiet necessary to analyze the whole class discourse. He divides the pedagogic discourse into two registers — the regulative and the instructional. The regulative register is about the overall ordering, sequencing and management of the discourse, which has to do with goals, purposes and directions of the teaching-learning activity. The instructional register is about the particular field of experience taken up in the pedagogic activity, which has to do with the “content” to be taught and learned. The relationship between them is that the operation of the former register determines the operation of the second. The two registers work together to show how students and teachers are built in the discourse and how students master the common knowledge. The relationship between the two registers is like the relationship between the knowledge and critical thinking.
...........................................
2.2 Critical Thinking
In today's society, innovation is the theme of the times and social life reflects the distinctive characteristics of innovation. Cultivating the innovative thinking of senior high school students is an important goal of the reform of senior high school education mode. Critical thinking is the key to the formation of objective rationality and an important part of innovative thinking, which plays an important role in the current education reform of ordinary senior high schools.
2.2.1 The Definition of Critical Thinking
Many scholars define critical thinking as skills, for example:
Paul (2000) thinks critical thinking is the art of analyzing and evaluating thought processes aimed to improve them. Critical thinking is self-directed, self-disciplined, self-monitored and self-corrective thinking. It entails efficient communication and problem solving abilities as well as a promise to conquer our native egocentrism and sociocentrism. He thinks a successful critical thinker can raise vital questions and problems, collect relevant information, acquire the skills of well-reasoned conclusion and communicate effectively and so on. What’s more, Fisher (2001) thinks CT is a generic term to all subjects which can be applied to reading, writing, speaking and listening. It’s useful in every domain of learning. It includes the disciplined analysis and assessment of reasoning as one cultivates intellectual virtues. It includes concern for two primary barriers to criticality—egocentric and sociocentric thinking—which are universal in human thought and life.
Glaser (1941) defines critical thinking as an attitude of being disposed to consider in a thoughtful way the problems and subjects that comes within bounds on one’s experience. He suggests people should make use of their own experience, regard CT as a matter of certain skills and encourage students to use them. Also Brook and Richard emphasize the importance of personal experience in CT. They think critical thinking is not to figure out the right thing but to evaluate what we experience. The key is to think about our thinking. The researcher thinks CT contains several skills. It's important to foster CT habit and improve CT skills which can make us intelligent. It’s composed of claims, issues and arguments. It's important to distinguish, analyze and evaluate these elements. (Brooke, 2012).

英语论文怎么写
................................
Chapter 3Theoretical Foundation ................................. 163.1 The Background and Development of Bakhtin’s Dialogism ............................... 16
3.2 The Main Content of Dialogism......................................... 17
3.3 The Application of Dialogism to Critical Thinking .............................. 18
Chapter 4 Research Design ......................................... 19
4.1 Research Questions ................................... 19
4.2 Research Participants................................. 20
4.3 Instruments ......................................... 21
Chapter 5 Results and Discussion ................................... 26
5.1 The Overall Level of Students’ Critical Thinking................................................ 27
5.1.1 The Level of Students’ Critical Thinking in Each Class........................... 27
5.1.2 The Depth of Students’ Critical Thinking in Ten Indicators..................... 32
5.1 The Overall Level of Students’ Critical Thinking
5.1.1 The Level of Students’ Critical Thinking in Each Class
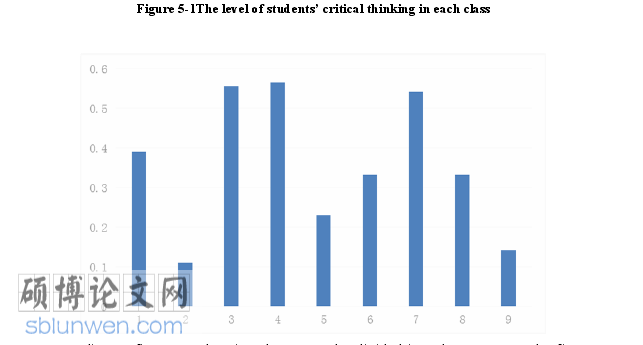
Through the interaction between students and teacher, the students’ discourse is coded in ten categories, the researcher collects the positive and negative value in each indicator. And the level of critical thinking in each class is calculated through the formula (X+-X-)/(X++X-). The level of nine classes is showed in the following figure.
英语论文参考
..........................
Chapter 6 Conclusion
6.1 Major Findings
From the previous study on data analysis of classroom discourse in nine classes, the major findings of students’ CT level are concluded as follows:
(1) The overall level of students’ critical thinking
Among the nine classes, the level of students’ CT is low, only three of them are above 0.5. Students’ critical thinking ability is relatively low. The reason is that students always answer in a single word because of their poor oral expression. Second, teachers usually have a discourse in a way of correct answer plus yes or no question which is more like monologue. So students have a habit of depending on the teacher. There is a few opposite opinions in class. Third there is no classroom environment to make students have enough opportunities to have authentic conversation. Last teacher places more emphasis on getting the information and the "skimming" of the text but not on the logical consistency, tone and organization.
Although students’ critical thinking level is low, they do well in R (relevance). Students can focus their attention to the problem. The depth of I (importance) is kind of low, students seldom come up with the important points or issues about the theme. Worst of all is the novelty, students can’t come up with new information, ideas and solutions. They prefer to follow teacher’s ideas. From the perspective of “O”, they seldom use their personal experiences and outside material to support their ideas.
It can be found in A (ambiguities) that students can seldom express their ideas clearly, they always make confused statements and ignore ambiguities. Also students seldom relate what they discuss to familiar situations and practical use. However, sometimes students do well in L (linking ideas), J (justification) and C (critical assessment). But sometimes they do nothing. And students never have a wide understanding of the issue in the nine classes.
reference(omitted)
