
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 Research Background
Pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar are the three basic elements in learning a language. The importance of speaking lies in whether language learners can apply the language they have learned to daily communication. Nowadays, the primary requirement for high school language learners is communicative competence. With the development of globalization, English, as the most important foreign language, has been attached great importance, while cultivating the communicative ability of students using English has become the ultimate goal of foreign language teaching. Pronunciation is the carrier and research basis of language communication. There are currently more than 5,000 languages in the world, and about two-thirds of themhave only pronunciation communication to the exclusion of textual inheritance. For the two language media of sound and text, the former must be given the dominant position. Celce-Muricia et al. (1996) pointed out that pronunciation plays a vital role in communication. The mistakes of learners in the segment and suprasegment may cause misinterpretation or communication barriers. Scholars in China and abroad all emphasize that attention should be paid to pronunciation teaching.
Chinese learners who acquire English as a foreign language generally view English grammar and pronunciation as the two barriers. Some learners can learn grammar well; however, their pronunciation turns out not so good. In other words, when Chinese learners open their mouth, they even couldn’t make themselves understood. It is noteworthy that students in English major also present an unsatisfactory pronunciation, leading to many troubles when they start a conversation with foreigners or have an interview to hunt for jobs. Therefore, great attention should be paid to pronunciation learning. Gimson (1970), a famous English pronunciation scholar, had his own description or understanding of pronunciation, “to speak any language, a person must know nearly 100% of its pronunciations, but only 50-90% of its grammar and 1% of the vocabulary.”
.......................
1.2 Importance of EPLS
In recent years, with the continuous development of politics, economy and culture in China and the constant enhancement of comprehensive national strength, English education can be said to have been risen to the level of national strategy. It is also reflected in the college entrance examination as the vane of the times. The test papers in Guizhou area are in three volumes in the whole country. The listening test is taken twice separately in September of the year before the college entrance examination and in March of the year of the college entrance examination, and the highest score is taken as the final score. All this suffices to show that the competent department of education attaches great importance to the listening part. Linguistics makes it clear that there is no separation between hearing and speaking. Students' own pronunciation will affect their judgment on the content of listening materials.
Unfortunately, due to insufficient time and heavy teaching burden in high school, it is difficult for teachers to use classroom time to train students' pronunciation. If students can find favorable methods to improve their pronunciation after class, it is of great significance to both teachers' listening teaching and students' college entrance examination results.
Therefore, it is of great significance to study students’ use of English pronunciation learning strategies (EPLS) at the basic education stage. At the same time, it also promises to assist teachers in listening teaching and improve students' listening performance.
......................
CHAPER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Definition of EPLS
The study of learning strategies began in the 1960s and has been a hot topic for researchers at home and abroad since then (Oxford 1990; O, Malley & Chamot 1990; Wen (1996). For the definition of LS, foreign linguists consider it a process, a psychological rule, and a specific method and skill. Several definitions have certain enjoyed consensus and universality.
Rubin (1975) considers it as the specific methods and means that language learners take to acquire knowledge of a second language.
Chamot (2004) takes it as the skills, methods, and behaviors students take to promote learning so as to enhance the memories of language information and content information.
O’Malley & Charmot (1990) argues that LS are special methods or behaviors that learners use to enhance their understanding, learning, or memorizing information.
Oxford (1990) argues that LS are some of the behavioral means that learners use to develop foreign language skills, and they are consciously used to develop communicative competence.
The above definitions show certain commonality, that is, taking learning strategy as a method or behavioral means used to complete a learning task.
Few scholars have given accurate definitions in the study of EPLS. Based on the definition of LS by Oxford (1990), Peterson (2000) defined pronunciation learning strategies as the methods and techniques used by language learners to improve their pronunciation learning consciously. This definition is also the one to be adopted in this study.
.........................
2.2 Classification of EPLS
Many studies in China and abroad have different classifications of LS. The most common classification method is the one given by Oxford (1990) and it is called the most comprehensive classification method (Hsiao & Oxford, 2002). Specifically, Oxford's Strategy Inventory for Language Learning (SILL) classification is as follows: LS are divided into two categories, indirect strategies (e.g., meta-cognitive strategy, emotional strategy, and social strategy), and direct strategies (e.g., memory strategy, cognitive strategy, and compensation strategy). Oxford gives its classification according to learning process.
Another foreign scholar, Cohen (2000), divided LS into language LS and language use strategies. Language LS include identifying and distinguishing learning materials, classifying materials and frequently contacting materials and memorizing materials. Language usage strategies include refining search, practice, compensation, and communication strategies.
Chinese scholar Wen (1996) divided LS into management strategies and language LS. The former includes planning, selecting different strategies, self-regulation, and self-management, while the latter includes language text materials and different forms of language training.
In the research results of LS, Peterson (2000) labeled his own pronunciation learning strategies according to Oxford's classification criteria. He divided pronunciation learning strategies into memory strategies, metacognitive strategies, affective strategies, social strategy, and compensation strategy, which was labeled as below:
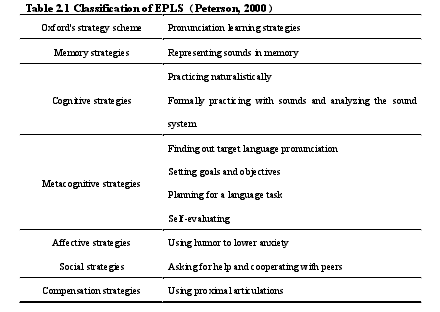
........................
CHAPER 3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY ..................................... 19
3.1 Research Design ......................... 19
3.1.1 Research Questions .............................. 19
3.1.2 Research Subjects ...................................... 19
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS ............................................ 27
4.1 Detection of Data Normal Distribution ..................................... 27
4.2 Students’ Use of EPLS ................................. 28
CHAPTER 5 DISCUSSION .......................................... 48
5.1 Senior High School Students' EPLSU ........................................ 48
5.2 Relationship Between EPLS and Mother Tongue ......................... 50
CHAPTER 5 DISCUSSION
5.1 Senior High School Students' EPLSU
As shown in the fourth chapter, the overall mean value of the students' use of the English language learning strategy is at a moderate level. The scores of metacognitive strategies are at a low level, and the other five dimensions (memory strategies, cognitive strategies, compensation strategies, emotional strategies, and social strategies) are at a medium level. Compensation strategies are scored the highest. In other words,compensation strategy is used more frequently, and the result is consistent with the studies by the Tang (2009) and Wen (2011). Judging from the item of single reading, there are 49 questions set in the questionnaire, of which 27 of them belong to the medium level, and 22 fall into the lower level. The item that obtained the highest score is item 4 (M = 3.40) and the item that obtained the lowest score is item 5 (M = 1.63), suggesting that the frequency of EPLS used by senior high school students is not high, which may be attributed to several reasons:
.......................
CHAPTER 6 CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS LIMITATIONS
6.1 Conclusions
The purpose of this study is to explore senior high school students’ use of EPLS, and propose suggestions for the improvement of students' PLS. Besides, this study also attempts to answer the four research questions
Major findings of this study were summarized in the following.
Researcher answered the first question with descriptive statistics. By analyzing the questionnaires collected, it can be known that the students' use of EPLS is generally at a medium level.
Independent sample t-test is used to analyze the data and thus answer the second question "Are there any significant difference between CS students and MS students? " Research results show that there is a significant difference in the use of EPLS between them. And the average score of MS students is higher than that of CS students, suggesting that MS students are better than CS students in the use of EPLS.
In order to answer the third question, correlation analysis and multiple regression analysis are used for the data collected. The results show that there is a correlation between frequency of pronunciation exercises and use of EPLS, and there is a significant correlation among metacognitive strategies, cognitive strategies and memory strategies.
reference(omitted)
