
Chapter 1 Introduction
1.1 Research Significance
In recent years, state-of-the-art computer vision systems made a lot of progress on object detection because of the use of convolutional neural networks (CNN) in their working. CNN has become the usual for image classification, image recognition, object detection and so on. In fact, since then, on ImageNet challenge, CNN has improved outperform and image classification is more facile than the difficulty and polarity of true human visual understanding. The role of convolutional neural networks is to reduce the images into a form which is easier to process, without losing features which are critical for getting a good prediction. CNN were chosen because it has the ability to develop an internal representation of a two dimensional image. This allows the model to learn position and scale in variant structures in the data, which is important when working with images. In classification, the main focus lies onto an image with a single object and the task is to classify what that image is. But in reality, it is the far more complex tasks. To adjust with the problems that are complicated with overlapping and backgrounds in an object, we might need to classify these different objects, identify boundaries, variances, and relations to one another. There are various types of object detectors developed in last few years such as, R-CNN, Fast R-CNN, Faster R-CNN, Mask R-CNN, R-FCN, SSD and YOLO which is deployed in different consumer products and some of the run on mobile devices. SSD Mobile Net is used in Google Photos and Pinterest Visual Search due to its speed and memory efficiency. But in the self-driving cars, the real-time performance and accuracy is the primary requirement where it can lead a life or death based on surrounding situations.
.........................
1.2 Research Objectives
In this era, researchers are working to find out a way in the arena of computer vision so that computers can see, recognize and process images in the similar way human vision ensures and afford appropriate output. It is like conveying human intelligence and instincts to a computer. Nevertheless, it is a tough task to enable computers to recognize images in dissimilar objects. To knob this problem, in computer vision object detection is an significant aspect because to detect objects detection is an ultimate issue. From the last century, there are many algorithms, models and structures are developed. After conquering all previous glitches, recently to detect objects from dissimilar scales there are many models developed such as DSSD, Faster R-CNN, FPN, STDN, Mask R-CNN, etc. which resolves the scale problems that lies in the core of object detection. Besides, recognizing objects at vastly dissimilar scales is a challenge in computer vision. The main research objective of this paper is to briefly compare the models which are described the feature maps and/or how to enlarge feature maps. In this paper, we generally focused on three feature extractor models such as bilinear interpolation, nearest neighbor interpolation and pixel shuffle to compare the average precision based on CNN analysis. The basis of choosing deep learning frameworks is that it allows us to build deep learning models more easily and quickly without getting into the details of underlying algorithms. Besides, it provides a clear and concise way for defining models using a collection of pre-built and optimized components which is capable for optimizing the performance, parallelize the processes to reduce computations and automatically compute gradients. Moreover, these retrospective algorithms are chosen because all the models are performed for image feature extraction by using CNN. Because detecting objects and categorizing the features from an image to predict objects at different scales, it is required to extract features or inject additional context information or integrate low-level and high-level features within a CNN to get more influential features to get the accurate output considering with the speed vs accuracy. Feature Pyramid Network (FPN) is a feature extractor designed for such pyramid concept with accuracy and speed in mind. It replaces the feature extractor of detectors like Faster R-CNN and generates multiple feature map layers (multi-scale feature maps) with better quality information than the regular feature pyramid for object detection. Based on the FPN, we modified the detection models as bilinear interpolation, nearest neighbor interpolation and pixel shuffle for comparing the different constraints like average precision only for the bounding box. One of the many so-called goals of ‘AI’ or machine learning is to describe a scene as precisely as a human being.
..........................
Chapter 2 Related Work
2.1 Datasets
In the area of computer vision, there are several types of datasets available. Among them, PASCAL VOC is an eminent dataset for object detection, image classification, object segmentation and so on. From 2005 to 2012, different challenges spread over with their own specifications and contains around 10,000 images for training and validation tests. PASCAL VOC is still enumerated as a standard reference of datasets in the object detection even though it contains only 20 categories.
Since 2013, another object detection dataset has released which is called ImageNet. It provides the bounding boxes in an image. Around 500,000 images are composed for training and a total of 200 categories available. Unfortunately, this dataset required huge computational power for training because of the size of the dataset as well as the high number of classes complicates the object recognition task. Therefore, it is hardly used in practical purpose.
Microsoft developed another dataset which is called Common Objects in Context (COCO). This dataset contains around 80 categories and composed more than 120,000 images for training and validation and more than 40,000 images for testing. This dataset is used for numerous challenges such as caption generation, object detection, key point detection, and object segmentation. The dataset now divided into two parts: one is used for a test-dev dataset for researchers and another test-challenge dataset for competitors.
...........................
2.2 Region-based Convolutional Neural Network (R-CNN)
The R-CNN model was one of the first apparition models of the convolutional network-based detection. The principal of this model is to take an image as input and correctly identify where the main objects located in the image. But using the straightforward approach a gap appears about the existence of bounding boxes. R-CNN provides a solution and propose a group of boxes in the image and find an object in accordance with the correspondence of boxes. Compared with the system based HOG-like features, R-CNN shows that it can lead advanced object detection performance on PASCAL VOC dataset. Basically, this model spontaneously starts with the region search and then accomplish the classification. In R-CNN, a region proposal algorithm called Selective Search was developed for object detection and is commonly used due to its fast and high memory among all other region proposal methods. To capture object location in an image firstly, it initializes small regions and then merges with a hierarchical grouping and final group creates a box containing the entire image. Though it seems different sizes of windows and for each size it merged according to a variety of color pixels by texture and similarity metrics. In Figure 2.1, the R-CNN feature extraction process shows step by step.
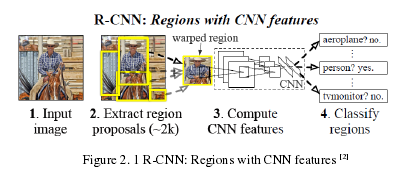
...........................
Chapter 3 Research Methods .............................................. 17
3.1 Feature Pyramid Networks ............................................ 17
3.1.1 Feature Pyramid Networks for RPN ........................................ 18
3.1.2 Feature Pyramid Networks for Fast R-CNN ................................. 19
Chapter 4 Experiment and Result ............................................. 28
4.1 Nearest Neighbor Interpolation ...................................... 28
4.2 Bilinear Interpolation ......................................... 29
4.3 Pixel Shuffle Interpolation ........................... 30
Chapter 5 Conclusion ................................... 33
5.1 Future Scope .............................. 34
Chapter 4 Experiment and Result
4.1 Nearest Neighbor Interpolation
To evaluate the nearest neighbor interpolation, first we train the dataset where in main papers, they used 90k epochs and we reduced the epochs as 60k to save the training time for faster training the model. After successfully training the model, it also generate some loss and total loss of mask rcnn benchmark is 0.5986 where bounding box regression loss is 0.1029 and loss classifier is 0.1872. We initialized the learning rate as 0.02 and the attention coefficient is 0.0001 in 40000 and 54000 iterations respectively. Our model loss the mask and objectness value as 0.2502 and 0.0257 respectively where bounding box regression with region proposal network is 0.0345. For every iteration, maximum memory consumes 4191. The evaluation is only based on bounding box. According to the evaluation of bounding box, we fixed the IoU in between 0.50 to 0.95 such as (IoU ~ 0.5-0.95) per image and then generated the result in total 5000 iterations and 18.11 iterations for per second. We also evaluated the prediction loading and preparing results by 2.08 seconds and the annotation type for bounding box evaluated in 44.65 second. Table 5.1 represents the accumulating evaluation results based on Average Precision, and table 5.2 represents the accumulating evaluation result based on Average Recall.
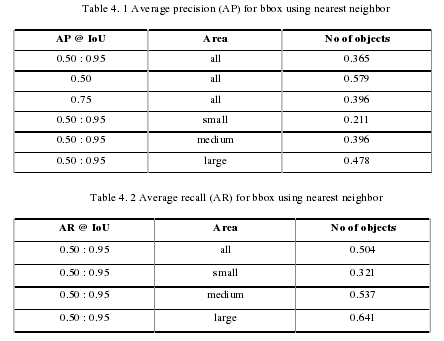
..........................
Chapter 5 Conclusion
We have performed and compared modern object detector models for the enlargement of feature maps which use convolutional neural networks with the direction of speed and accuracy. So far, all the models have worked better and widely used in the area of object detection. In general, it is quite hard to choose the appropriate method for deploying object detection and it will help the practitioners to improve the speed and accuracy with the observations of this paper. However, all the methods are performed on COCO 2014 minval dataset with different combinations and discovered better results with different aspects for feature extractor in object detection. Thus, the proposed method showed significant improvements over several strong baselines and competition winners. Our analysis provides a practical solution for research and applications of feature pyramids, without the need for computing image pyramids. Finally, our study suggests that despite the strong representational power of deep ConvNets and their implicit robustness to scale variation, it is still critical to explicitly address multiscale problems using pyramid representations. The FPN was used in FRCNN in both parts of RPN and RCNN separately and then combined FPN in both parts and produced the state-of-the-art result in MS COCO challenges for better results of COCO '15 & '16 winner models ( Faster RCNN +++ & GMRI) for mAP. FPN also can be used for instance segmentation by using fully convolutional layers on top of the image pyramids. FPN outperforms results from DeepMask, SharpMask, InstanceFCN. Though, in Faster R-CNN, FPN improves recall on COCO by about 8 points, compared to using standard RPN and improvement becomes stronger for small objects. Only RPN uses some convolutions to transform each feature map into region proposals which improves the features of these convolutions marginally. On the other hand, from our analysis, we can state that the overall accuracy of three up-sampling methods, nearest upsample, bilinear upsample and pixel shuffle upsample, is comparable in all scales of object detection. However, for three scales of object detection, feature extraction of nearest upsample is more suitable for large-scale object detection and bilinear upsample is more suitable for medium-sized target detection. In addition, pixel shuffle upsample performs well in three scales of target detection, especially in small target detection, because compared with the other two explicit interpolation sampling methods, this method can implicitly learn. The results of the other three up-sampling methods are similar in recall index. We can conclude that; the accuracy by using different methods are similar with each other but pixel shuffle interpolation improves the result for small feature objects.
reference(omitted)
