CHAPTER ONE INTRODUCTION
1.0 Overview
This study aimed to explore out-of-field novice teacher resilience and its influencing factors. Therefore, the current chapter comprises the background of the problem, statement of the problem, purpose, and objectives of the study, research questions, significance of the study, delimitation of the study, and operational terms.
Zanzibar consists of two islands (Unguja and Pemba) which united with Tanganyika to form the United Republic of Tanzania on 26th April 1964. But Zanzibar remains a semi-autonomous country and the issue of education is controlled by the Revolutionary Government of Zanzibar (RGoZ). Before independence education situation in Zanzibar was characterized by racial discrimination, classes and expenses hence most of Zanzibaris could not meet the expenses.
Soon after independence (1964), the RGoZ started to invest in the education sector. During the 1984’s the RGoZ proclaimed free Education for all Zanzibaris irrespective of color and gender differences. Since then, education in Zanzibar took different changes in advancements and improvements to cope with international demands and declarations for education development, such as Education for All (EFA) and Millennium Development Goals (MDGs). Compare to neighboring countries, Zanzibar has been reported to rank as the country with the second-highest percentage of the education budget in East Africa by 18.1% after Kenya with 25.0% whereas Rwanda at 16.6%, and Uganda at 11.8% (Zanzibar Education Budget Brief, 2018). Therefore, access to quality education tends to rise year after year due to good educational policies such as access to Higher Education, and the availability of Public and Private Universities and Colleges that provide teachers’ education (Zanzibar Education Policy (ZEP), 2006).
.......................
1.2 Teaching Experience of Novice Teachers
In adapting to the new working environment, novice teachers in their early years are expected to utilize the learned knowledge and creative ideas in teaching activities. However, the majority of novice teachers including out-of-field novice teachers have been reported to experience demands of more time, support, training, and mentoring so that they can manage classrooms, relationships, and planning (Ingersoll, Merrill & Stuckey, 2014;Shields, 2020). Du Plessis et al. (2015) contended that out-of-field novice teachers cannot perform their teaching roles effectively without “specialized intensive support from staff development programs”.
Besides, diversity of situations like how to address chronic and disruptive students’ behaviors issues that novice teachers need to be assisted to handle (Ferlazzo, 2014). It is delineated that, as novice teachers strive to become accustomed to the learning community, they necessitate learning how to nurture and build capacity that enhances resilience during their early stage of teaching. Due to meager knowledge on curriculum and content mastery, out-of-field novice teachers noticeably require some coping strategies to figure out (Du Plessis et al., 2015; Ortega, Luft & Wong, 2013; Pacana et al., 2019).
Correspondingly, stress and frustration on standardized testing are among the experiences that novice teachers as well as out-of-field novice teachers encounter in the profession leading to emotional exhaustion (Calams, 2015; Du Plessis et al., 2015). To overcome this, they require greater knowledge and enthusiastic ability to ensure that tests are well constructed to meet the required standards and thus guaranteeing the academic development of students (Calams, 2015; Cross & Hong, 2012).
Generally, the development of personal and professional dispositions, coping strategies, and professional networks are very crucial in assuring that out-of-field novice teachers attain the standard of teaching (Morgan, 2011). Support networks such as expert teachers is needed to play an effective role in assisting novice teachers (including out-of-field) to be well fortified in teaching through induction and mentoring programs which ultimately embolden them as well as enabling to withstand in the teaching profession.
............................
CHAPTER TWO LITERATURE REVIEW
2.0 Overview
The purpose of this study was to explore the out-of-field novice teacher resilience and its influencing factors. Therefore, in this chapter, the researcher explains the definition of novice teacher, the conceptualization of resilience, teacher resilience, resilience characteristics, and factors influencing out-of-field novice teacher resilience, challenges facing them, and strategies to overcome their challenges. Also, this chapter includes the theoretical and conceptual framework of this study based on research objectives.
2.1.0 Key Concepts
2.1.1 Novice teachers
The term novice teacher in this study is the one who typically has less than five (5) years in teaching profession. However, literature pointed out that, there are no general agreements on the definition of a novice teacher. Different countries and researchers have various criteria in defining a novice teacher. In New Zealand for example, a newly qualified teacher remains as a novice teacher for the first two years of teaching (Brunton, 2011 as cited in Ngang at al., (2014)). Conversely, novice teachers in Australia are those who have less than three years of teaching experience (Archived Reports, (2007) as cited in Ngang at al., (2014)).
In Zanzibar, novice teachers are those teachers after completion of College/University training, they undergo orientation for one year upon being employed and to be certified by MoEVT. In light of this study, out-of-field novice teachers are those teachers with less than five years of teaching experience and they teach science subjects outside of their fields. In this regard, Zanzibar’s novice teachers in their first years of teaching struggle with little experience obtained during Block Teaching Practice (BTP). Therefore, they are required to complete one year orientation period to acquire teaching experience and to have job satisfaction. It is well understood that teaching is a more complex work especially to novice teachers, and teacher preparation programs are not sufficient to provide essential skills and knowledge for effective teaching. Therefore, after being employed novice teachers develop teaching competency and other necessary skills to ensure good instructional practices in classrooms and academic success of students. In achieving this schools should prepare a good working environment for novice teachers to develop a fully teaching competency.
............................
2.2.0 Characteristics of Out-of-field Novice Teacher Resilience
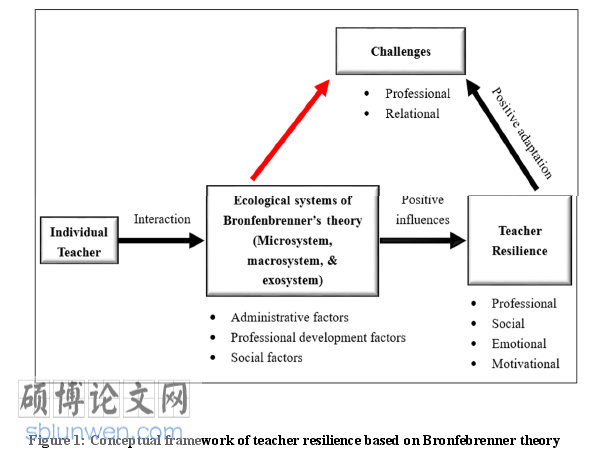
For a teacher to be resilient, he/she must demonstrate certain features, and these features have been discussed in different studies. According to Mansfield et al. (2012) in their study “Don’t sweat the small stuff:” Understanding teacher resilience in the Chalkface” they classified characteristics of teacher resilience into four major dimensions. They include the professional, social and emotional, and motivational-related dimensions.
2.2.1 Professional Characteristics
Professional-related characteristics of a resilient teacher include those connected to teaching practices such that the teacher is well organized, prepared, and managing time properly (Mansfield et al., 2012). A resilient teacher is who is creative and artistic in teaching, can engage in professional learning, being reflective in teaching, committed to students, and flexible and adaptable (Bowles & Arnup, 2016; Mansfield et al., 2012; Tait, 2008). These researchers contended that these professional characteristics enable novice teachers to increase their commitment to teaching despite threatening circumstances. For this study, the said professional characteristics of resilience may be exhibited by out-of-field novice teachers in Zanzibar. For example, they involve themselves in professional learning as a strategy to increase their professional knowledge and competence in the subject area they are assigned to teach.
2.2.2 Social Characteristics
In this aspect, the resilience characteristics associated with social interactions such as the positive relationships between out-of-field novice teachers with other staff members, head of schools, friends, and families. Resilience characteristics such as asking for assistance and advice, problem-solving skills, strong interpersonal and communication skills (Mansfield et al., 2012, p.362; Tait, 2008) can be demonstrated by out-of-field novice teachers in their working environment. For example, out-of-field novice teachers may seek assistance or advice from veteran teachers concerning their classroom teaching such as how to prepare lesson plans and the use of instructional strategies. Similarly, through collaborative relationships experienced teachers act as mentors to out-of-field novice teachers in professional development activities to increase competence in teaching (Pacana et al., 2019). Thus, social interactions within and outside the working place enhance out-of-field novice teachers’ efficacy which in turn strengthen their capacity to adjust to various encountered challenges.
CHAPTER TWO LITERATURE REVIEW
2.0 Overview
The purpose of this study was to explore the out-of-field novice teacher resilience and its influencing factors. Therefore, in this chapter, the researcher explains the definition of novice teacher, the conceptualization of resilience, teacher resilience, resilience characteristics, and factors influencing out-of-field novice teacher resilience, challenges facing them, and strategies to overcome their challenges. Also, this chapter includes the theoretical and conceptual framework of this study based on research objectives.
2.1.0 Key Concepts
2.1.1 Novice teachers
The term novice teacher in this study is the one who typically has less than five (5) years in teaching profession. However, literature pointed out that, there are no general agreements on the definition of a novice teacher. Different countries and researchers have various criteria in defining a novice teacher. In New Zealand for example, a newly qualified teacher remains as a novice teacher for the first two years of teaching (Brunton, 2011 as cited in Ngang at al., (2014)). Conversely, novice teachers in Australia are those who have less than three years of teaching experience (Archived Reports, (2007) as cited in Ngang at al., (2014)).
In Zanzibar, novice teachers are those teachers after completion of College/University training, they undergo orientation for one year upon being employed and to be certified by MoEVT. In light of this study, out-of-field novice teachers are those teachers with less than five years of teaching experience and they teach science subjects outside of their fields. In this regard, Zanzibar’s novice teachers in their first years of teaching struggle with little experience obtained during Block Teaching Practice (BTP). Therefore, they are required to complete one year orientation period to acquire teaching experience and to have job satisfaction. It is well understood that teaching is a more complex work especially to novice teachers, and teacher preparation programs are not sufficient to provide essential skills and knowledge for effective teaching. Therefore, after being employed novice teachers develop teaching competency and other necessary skills to ensure good instructional practices in classrooms and academic success of students. In achieving this schools should prepare a good working environment for novice teachers to develop a fully teaching competency.
............................
2.2.0 Characteristics of Out-of-field Novice Teacher Resilience
For a teacher to be resilient, he/she must demonstrate certain features, and these features have been discussed in different studies. According to Mansfield et al. (2012) in their study “Don’t sweat the small stuff:” Understanding teacher resilience in the Chalkface” they classified characteristics of teacher resilience into four major dimensions. They include the professional, social and emotional, and motivational-related dimensions.
2.2.1 Professional Characteristics
Professional-related characteristics of a resilient teacher include those connected to teaching practices such that the teacher is well organized, prepared, and managing time properly (Mansfield et al., 2012). A resilient teacher is who is creative and artistic in teaching, can engage in professional learning, being reflective in teaching, committed to students, and flexible and adaptable (Bowles & Arnup, 2016; Mansfield et al., 2012; Tait, 2008). These researchers contended that these professional characteristics enable novice teachers to increase their commitment to teaching despite threatening circumstances. For this study, the said professional characteristics of resilience may be exhibited by out-of-field novice teachers in Zanzibar. For example, they involve themselves in professional learning as a strategy to increase their professional knowledge and competence in the subject area they are assigned to teach.
2.2.2 Social Characteristics
In this aspect, the resilience characteristics associated with social interactions such as the positive relationships between out-of-field novice teachers with other staff members, head of schools, friends, and families. Resilience characteristics such as asking for assistance and advice, problem-solving skills, strong interpersonal and communication skills (Mansfield et al., 2012, p.362; Tait, 2008) can be demonstrated by out-of-field novice teachers in their working environment. For example, out-of-field novice teachers may seek assistance or advice from veteran teachers concerning their classroom teaching such as how to prepare lesson plans and the use of instructional strategies. Similarly, through collaborative relationships experienced teachers act as mentors to out-of-field novice teachers in professional development activities to increase competence in teaching (Pacana et al., 2019). Thus, social interactions within and outside the working place enhance out-of-field novice teachers’ efficacy which in turn strengthen their capacity to adjust to various encountered challenges.
...............................
CHAPTER THREE METHODOLOGY ........................................... 323.0 Overview ................................................. 32
3.1 Research Design ......................................... 32
3.2 Area of the Study................................... 32
CHAPTER FOUR FINDINGS ............................................... 40
4.0 Overview ............................................. 40
4.1.0 Challenges Facing Out-of-Field Novice Teachers in Teaching ............................ 40
4.1.1 Professional Challenges ...................................... 40
4.1.2 Relational Challenges ...................................... 45
DISCUSSION, CONCLUSION, RECOMMENDATIONS, AND LIMITATIONS ........ 66
5.0 Overview ........................................ 66
5.1 Critical Challenges Facing Out-of-Field Novice Teachers in Teaching .................. 66
5.1.1 Shortage of Content Knowledge and Pedagogical Skills ...................................... 66
5.1.2 Difficulties on Syllabus Interpretation and Lesson Planning ................................ 68
CHAPTER FOUR FINDINGS
4.0 Overview
The general purpose of this study was to explore the out-of-field novice teacher resilience and its influencing factors. Thus, previous chapters presented the theoretical part of the present study. Therefore, this chapter presents the remaining empirical part of this study. Findings presented systematically based on the research questions. The questions were analyzed into themes and subthemes with what has been said by respondents from the interview and FGD.
4.1.0 Challenges Facing Out-of-Field Novice Teachers in Teaching
In this context, the first research question that the researcher needed to understand from the current study was, what critical challenges do out-of-field novice teachers experience in teaching? Based on the responses from the respondents, critical challenges are classified into two major themes with respective sub-themes. The major themes include professional challenges and relational challenges.
4.1.1 Professional Challenges
These are the challenges facing out-of-field novice teachers in classroom practices. They are categorized into four sub-themes which include; shortage of content knowledge and pedagogical skills, difficulties on syllabus interpretation and lesson planning, lack of classroom management skills, and pressure of curriculum load.
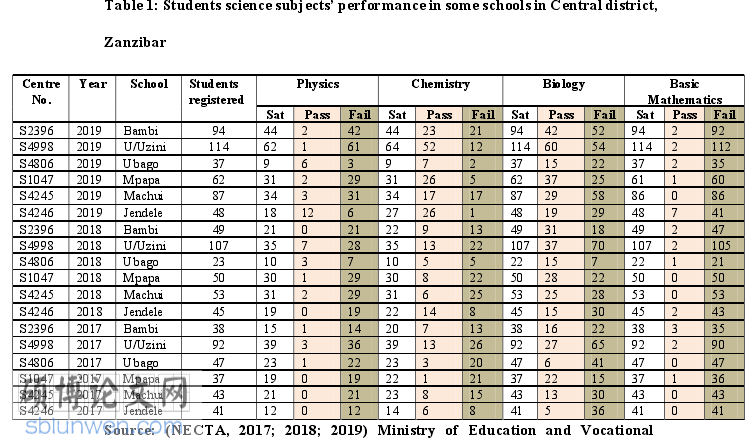
Shortage of content knowledge and pedagogical skills is one of the noticeable challenge facing out-of-field novice teachers. Novice teachers who are assigned in out-of-field positions have both shortages of Content Knowledge (CK) and Pedagogical Content Knowledge (PCK) in teaching. Meaning that, their content in their current teaching subjects including Physics, Chemistry, Biology, and Basic Mathematics is not enough to the extent that they do not feel competent in some of the science concepts because they experience incoherence in their actions and interactions arising from limitations in their CK and practices. Adequate CK and PCK enable teachers to deliver quality education to learners. Similarly, sufficient CK and PCK help a teacher to diagnose effectively students’ misconceptions within a particular subject. Respondents from the present study identified that, they feel incompetent and less self-confident due to a shortage of CK in subjects they are assigned to teach. These teachers also lack suitable PCK in delivering the content to ensure maximum understanding of the students. Therefore, they become nervous and unhappy when they fail to clarify students’ misconceptions during lessons.
...............................
CHAPTER FIVE DISCUSSION, CONCLUSION, RECOMMENDATIONS, AND LIMITATIONS
5.0 Overview
The general purpose of this study was to explore the out-of-field novice teacher resilience and its influencing factors. Therefore, the discussion of the results, conclusion, recommendations, and limitations of this study are highlighted in this chapter. Concerning the research questions, the researcher started by discussing the critical challenges that out-of-field novice teachers experience in teaching. Following by resilience characteristics demonstrated by out-of-field novice teachers when encountered challenges. And finally, the contextual factors that influence out-of-field novice teacher resilience to adjust from various encountered challenges.
5.1 Critical Challenges Facing Out-of-Field Novice Teachers in Teaching
In this study, the most critical challenge that out-of-field novice teachers experience in teaching was a shortage of content knowledge and pedagogical skills. Other challenges include difficulties in syllabus interpretation and lesson planning, lack of classroom management skills, and pressure of curriculum load, poor relationship with students, and poor relationship with head of the schools. These challenges mostly affect out-of-field novice teachers’ efficacy, commitment, and resilience in teaching.
reference(omitted)
The general purpose of this study was to explore the out-of-field novice teacher resilience and its influencing factors. Therefore, the discussion of the results, conclusion, recommendations, and limitations of this study are highlighted in this chapter. Concerning the research questions, the researcher started by discussing the critical challenges that out-of-field novice teachers experience in teaching. Following by resilience characteristics demonstrated by out-of-field novice teachers when encountered challenges. And finally, the contextual factors that influence out-of-field novice teacher resilience to adjust from various encountered challenges.
5.1 Critical Challenges Facing Out-of-Field Novice Teachers in Teaching
In this study, the most critical challenge that out-of-field novice teachers experience in teaching was a shortage of content knowledge and pedagogical skills. Other challenges include difficulties in syllabus interpretation and lesson planning, lack of classroom management skills, and pressure of curriculum load, poor relationship with students, and poor relationship with head of the schools. These challenges mostly affect out-of-field novice teachers’ efficacy, commitment, and resilience in teaching.
reference(omitted)
