CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
1. 1. Background of Study
Prowess and progress of a country are seen from the economic development in the country. However, many people forget the role of education can also encourage the development in every country. Research has shown the quality of human resources in a country is an important factor that can accelerate economic growth and development of that country. Education is a very important thing which demands the attention to government and the entire society gets attention on both the government and society in the country. Without education, a country will never experience development. Education is one of the most powerful instruments for reducing poverty and inequality and lays a foundation for sustained economic growth. Education is the driving force which helps countries to properly integrate itself into the rest of the world.
In the economic and technological globalization, driven by trading in service has increasingly become an important force affecting national economic development. The signing of the General Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS) has further accelerated the process of liberalization of international trade in service, and the momentum of trading in service has become stronger. According to the GATS negotiated in the Uruguay Round, trade in service refers to international trade in service, which is different from domestic trade in service.
According to the United States department of agriculture, educational attainment of rural America reached a historic high in 2000, with nearly one in six rural adults holding a four years’ college degree, and more than three in four completing high schools, it is not surprising that America is the most developed country in the world. Studies have shown that Singapore is a small country with total population in June 2015 is 5.54 million, which has a little population compared with Indonesia but Singapore is better and more advanced than Indonesia, as well as with other countries such as Japan and others. Singapore which according to studies, were not internationally recognized until recent years Singapore is now considered one of the countries that has successfully promoted itself in the international front and being representative of the ASEAN community.
.............................
1. 2. Literature Review
According the UNESCO definition, international students are students that have left their country of origin and moved to another country for the purpose of study. In the economic literature, international students are often seen as a potential inflow of human capital for receiving country (Murat, 2014). Le (2010) and Park (2004) evidence that, under certain situation, international students may also generate benefits for the sending economy. From this perspective, the main aim of investigation is that of shedding light on the determinants of students’ choices of whether to study aboard, and if so, where to study, and the consequences of potential brains gain for the host county. Many international students also choose where to study based on where they hope to start their careers (Obst, 2013). Asia is one of the fastest growing destinations for international students, and foreign enrollment universities in Indonesia and South Korea have more than doubled since 2005 (Sheehy, 2013). Murat (2014) has shown that the international movement towards students can be an effective way of improving the economic exchanges of the countries involved.
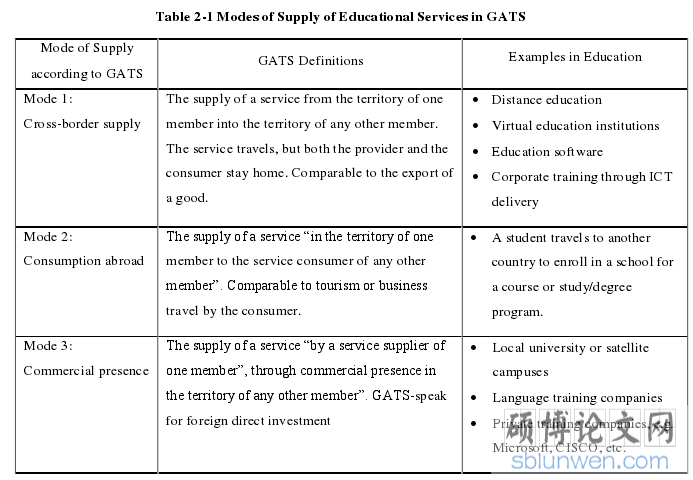
1.2.1. Related to Education Service Trade
The signing of The GATS has further accelerated the process of liberalization of international trade in service, and the momentum has become stronger. The classification of the International Educational Services Trade is based on the United Nations Center for Product Classification System and is identified as 12 basic services sectors, namely, commercial services, communications services, construction services, marketing services, education services, environmental services, financial services, health and social services, tourism and related services, culture, entertainment and sports services, transportation services and other services (Bin, 2004).
..........................
CHAPTER 2 THEORETICAL FOUNDATION
2. 1. The Concept of Trade in Services and Education
The traditional pure theory of international trade is based on the commodity (goods, physical) trade. Therefore, strictly speaking, service trade does not form its own theoretical system. However, the practice of service trade development calls for the birth of service trade theory. There are two options for establishing a relatively complete service trade theory system. The first is to develop a relatively independent service trade theory based on the practice and characteristics of international service trade and to draw on the research results of related disciplines.
The second is to extend the traditional theory of merchandise trade to the field of service trade, and use corresponding logic and concepts to explain service trade, so as to achieve the docking of the theory of goods trade and service trade. Judging from the actual development of the service trade theory, the theoretical community is more inclined to the second option. This is not only because the first choice has practical difficulties, but more importantly, when people make the first choice and try to establish a relatively independent pure theory of service trade, they cannot completely break with the traditional theory of merchandise trade. The result is involuntarily back to the second option.
Service trade is a service exchange behavior, generally refers to the international trade in services. Service trade has a variety of content, such as trade in educational services. Educational services are educational activities of a commercial nature that charge tuition fees, excluding teaching activities that are fully funded by governments. Education service trade is the export and import of educational services for economic purposes between countries.
............................
2. 2. Theory of International Competitiveness
Economists usually use many ways in seeing or identifying the competitiveness of a commodity or service in the domestic and international markets. International competitiveness is a process in which higher levels of competitiveness are achieved at different levels (firm, regional and national levels). Competitiveness is a measure of a country's advantage or disadvantage in selling its products in international markets. Competitiveness becomes international when it concerns to two or more countries. Such process is captured by definitions of competitiveness which move from a general perspective to more specific understandings at the firm and country levels. There are several definitions of competitiveness that must be considered before one can build a particular understanding of international competitiveness.
2.2.1. The Definition of International Competitiveness
Buckley, Pass, & Prescott (1988) argued that international competitiveness can be understood as the balance between efficiency and effectiveness in the economic realm. Others build an understanding of competitiveness at the firm-level. For example, the report of the select committee of the house of lords on overseas trade focuses on the competitiveness of enterprises. According to Buckley, Pass, & Prescott (1988) argued that international competitiveness can be understood as the balance between efficiency and effectiveness in the economic realm. Others build an understanding of competitiveness at the firm-level. For example, the report of the select committee of the house of lords on overseas trade focuses on the competitiveness of enterprises.
..............................
CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF DEVELOPING PROCESS AND CURRENT SITUATION OF INDONESIA’S HIGHER EDUCATION SERVICE TRADE .................... 22
3. 1. The Regulation and Policy of Indonesia’s Higher Education Service Trade .................. 22
3. 2. The Development of Indonesia’s Higher Education Institutions ..................................... 27
CHAPTER 4 COMPARATIVE STUDY ON INTERNATIONAL COMPETITIVENESS OF INDONESIA’S HIGHER EDUCATION SERVICES TRADE ......................................... 42
4. 1. International Market Share (IMS) ...................................... 42
4. 2. Trade Competitiveness Index (TCI) ............................ 45
CHAPTER 5 ANALYSIS OF THE FACTORS AFFECTING THE COMPETITIVENESS OF INDONESIA’S HIGHER EDUCATION SERVICE TRADE ........................................... 54
5. 1. Description of Analysis ......................................... 54
5. 2. Analysis of Sample .............................. 54
CHAPTER 6 RECOMMENDATION ON IMPROVING THE COMPETITIVENESS OF HIGHER EDUCATION SERVICE TRADE IN INDONESIA
6. 1. Improve The Promotion of Indonesian Culture
The introduction of a country's culture in another country has a positive impact on the two countries socially, economically, and educationally. To improve the country's competitiveness in the field of higher education service trade, culture must also be an important factor that determines one's interest in continuing studies in that country, because culture indirectly also teaches non-formal education for a person. Cultural introduction can be done through public diplomacy or cultural diplomacy and second track diplomacy. Cultural diplomacy is one of the tools used by a country in achieving national interests in other countries by involving various soft fields such as education, arts, culinary, and sports. This diplomacy aims to make people who are abroad support the existence of diplomacy policies held by a particular country aimed at his country. This diplomacy can be carried out by government or non-government which includes individuals and organizations.
While the second track diplomacy, can be interpreted as the efforts of the role of individuals or citizens in carrying out their role in making approaches and introducing culture to foreign communities so that the culture can be accepted. This diplomacy does not mean that they replace the role of first track diplomacy, but they are only intermediaries in carrying out diplomacy policies held by a country. Through ways of introducing culture, Indonesia can increase the attractiveness of other countries, increase the international competitiveness, and can even increase the investment in Indonesia. If people who come from abroad are interested in Indonesian culture, they will also be interested in getting to know Indonesia more deeply by visiting Indonesia and even studying in Indonesia, and this certainly can increase the country's foreign exchange and have a stable competitiveness in the market international.
..............................
CHAPTER 7 CONCLUSION, LIMITATION, AND FUTURE RESEARCH
7. 1. Conclusion
The rationale of this study research is to examine the strength of international competitiveness of Indonesia's higher education service trade and the factors that affected to it by using comparative study which the time series data covered the period from 2001-2017 and empirical study using the response of questionnaire data from 302 participants. Based on the results of the research, it has shown that the condition of education service trade in Indonesia experiences an imbalance every year.
However, based on the results of research conducted through comparative studies using IMS, TCI, and RCA measurement methods, it can be proven that Indonesia has competitiveness that is equivalent to international standards, where the results are balanced between the number of foreign students coming to Indonesia with the number of Indonesian students who are going abroad to pursue higher education.
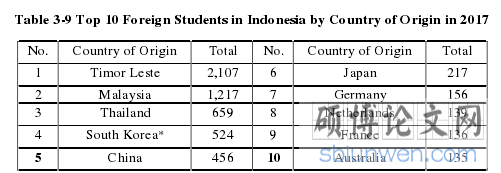
For the distribution of higher education service trade in Indonesia is still very small, this is due to economic inequality in Indonesia. This is evidenced from the number of educational institutions and the number of foreign students who are more in Jakarta and Java compared to other regions throughout Indonesia. About the selection of professional fields, it was proven that they did not have a significant effect on the competitiveness in the education service trade aspect. The factors that most directly influence the international competitiveness for higher education service trade are culture, quality of higher education and the cost of living in the destination country.
reference(omitted)
